Scheme of heating 2 storey house. Collector heating system. Short description of household radiators
The system of independent heating private a country house - in itself is very difficult to plan and implement the project. It is required to take into account a lot of nuances, to carry out the necessary heat engineering calculations, to choose the right equipment for the system by type and technical specifications, determine the schemes of its installation and laying the necessary communications, correctly perform the installation and conduct commissioning work. All this is done to ensure that the creation in living quarters the most optimal microclimate was fully combined with the simplicity of operation of the heating system, its failure-free operation and, without fail, with the greatest possible economy.
Well, if a heating scheme for a 2-storey private house is being developed, the task becomes even more difficult. Moreover, the number of rooms and the length of the thermal routes increase. It is important to achieve the necessary even distribution of heat across all premises, regardless of whether they are located on the floor or what area they have.
In this publication, the main elements of the private house heating system will be considered and several schemes that have already been tested in operation are listed. Of course, it is necessary to mention the advantages and disadvantages of each option.
What are the heating systems?
Open and closed heating systems
First of all, it is necessary to consider and compare the two basic schemes - heating systems of open and closed type. What is their main difference?
The coolant circulates through the pipes - a liquid with a high heat capacity, transferring heat energy from the place of heating - the boiler, to heat exchange points - radiators, convectors, contours of warm floors, etc. Like any physical body, the liquid has the property of expansion as the temperature rises. But, unlike, for example, gases, it is an incompressible substance, that is, the emerging surplus volume is tedious to provide a place so that the pressure in the pipes, according to the laws of thermodynamics, does not increase to critical values.
For this, an expansion tank is provided in any heating system with a liquid coolant. Its design and installation site also predetermines the separation of heating systems into closed and open systems.
- The principle of the open heating system is shown in the diagram:

1 - a heating boiler.
2 - feed pipe (riser).
3 - expansion tank of an open type.
4 - radiators of heating.
5 - pipe "return"
6 - pump unit.
The expansion tank is an open container of factory or handicraft production. It has an inlet branch pipe that is connected to the feeder riser. Can be supplemented with nozzles to prevent overflow during filling the system, to fill the lack of coolant (water).

The main condition - the expansion tank itself should be installed at the highest point of the system. This is necessary, firstly, in order to ensure that the surplus of the coolant simply does not pour out through the rule of communicating vessels, and secondly, it serves as an effective air purifier - All the gas bubbles formed during the operation of the system rise upward and freely escape into the atmosphere.
Under No. 6, the diagram shows a pump unit. Although very often open systems are organized according to the principle of natural circulation of the coolant, the installation of the pump - never hurts. Moreover, if you tie it correctly, with a bypass loop and stopcocks - this will make it possible to switch from natural circulation to forced circulation as needed and back again.

By the way, the installation of an open expansion tank it is at the top of the feed pipe - it is not at all an obligatory rule. There are possible options, the choice of which is based on the specific features of a particular heating system:

a - the tank is located at the highest point of the main supply pipe, which extends from the boiler. You can say - the classic version
b - the expansion tank is connected by a pipe with a "return". Sometimes it is necessary to resort to such an arrangement, although it has a significant drawback - the tank does not perform the full functions air vent, and to avoid gas jams, such a device will have to install special cranes on risers or directly on radiators.
c - the tank is installed on the far riser.
d - a rarely occurring arrangement of the tank with the pump unit immediately after it on the supply pipe.
- Below is a diagram of a closed-type heating system:

The numbering of common elements is preserved by analogy with the previous scheme. What are the main differences?
The system has a sealed expansion tank (7), which has a special design. It is divided by a special elastic membrane into two halves - a water and an air chamber.

Such a tank is very simple. With the thermal expansion of the coolant, its surplus falls into closed tank, increasing the volume of the water chamber by stretching or deforming the membrane. Accordingly, the pressure in the opposite air chamber increases. As the temperature decreases, the air pressure pushes the heat transfer fluid back into the pipes of the system.
Such an expansion tank can be installed almost anywhere in the heating system. Very often it is located in close proximity to the boiler on the pipe "reverse".
Since the system is completely sealed, it is necessary to protect against a critical increase in pressure in it in case of emergency situations. This stipulates that one more element is required: a safety valve that is set to a certain threshold. Usually this device is included in the the so-called "security group" (in the scheme - № 8). Its standard equipment includes:

The "security group" in the collection
1 – control and measuring device for visual monitoring of the state of the system: a manometer or a combined device - a manometer-thermometer.
2 - automatic air vent.
3 – safety valve with presetting the upper pressure threshold or with the possibility of self-regulation of this parameter.
The security team is usually placed in such a way that it is easy to monitor the state of the system. Often, it is installed right next to the boiler. In this case, the upper sections of the heating system will require additional air vent on risers or on radiators.
Systems with natural and forced circulation
The principles of natural and forced circulation have already been mentioned in passing, but it is worth taking a closer look at them.
- The natural movement of the coolant along the heating circuits is explained by the laws of physics - the difference in the density of hot and cooled liquids. To understand the principle, let's take a look at the diagram:

1 - point of primary heat exchange, boiler, where the cooled coolant receives heat from external sources of energy.
2 - supply pipe for the heated coolant.
3 - secondary heat exchange point - radiator installed in the room. It must be located above the boiler by an amount h.
4 - pipe "reverse, going from the radiators to the boiler.
The density of the hot liquid (Pg0) is always considerably less than the cooled (Rokhl). The heated coolant, therefore, can not have any significant effect on the denser substance. Therefore, it is possible to conditionally remove the upper "red" part of the scheme, and consider the processes in the "return" pipe.
The "classical" communicating vessels are obtained, one of which is located above the other. Such a hydraulic system always strives for equilibrium - to ensure an equal level in both vessels. Due to the excess of one over the other in the return pipe, there is a constant flow of liquid in the direction of the boiler. Such a natural way of creating the pressure with proper planning of the wiring is sufficient for the general circulation of the coolant along a closed heating circuit.
The higher the value of the radiators above the boiler (h),the more active the natural movement of the liquid, but it should not exceed 3 meters. Very often, in order to achieve an optimal location, the boiler is installed in a basement or basement room. If this is not possible, then try to slightly lower the floor level in the boiler room.
To facilitate and stabilize natural circulation, it is also assisted by gravity - all the pipes of the contour are arranged with a slope (from 5 to 10 mm per running meter).
- The forced circulation system provides for the mandatory installation of a special electric pump of the required capacity.
As already mentioned, the system can be combined - a properly tied pump will allow switching from one circulation principle to another. This is especially important in cases where the supply of electricity in the area of residence is not stable.
The optimal location for the pump is the return pipe in front of the boiler. This, of course, is not dogma, but on this site it will be less exposed to the influence of high temperatures of the coolant and will last longer. Currently, more and more purchased heating boilers, which constructively already contain a circulation pump with the required parameters.
Advantages and disadvantages of different systems
First of all, it should be noted that there is no clear separation of systems from the two mentioned parameters. Thus, an open system can work according to the principles of both natural and forced circulation, depending on its own constructive features. The same can to some extent be said about a closed sealed system, although already - from certain assumptions.
But if we consider the projects presented on the Internet, it can be seen that an open system more often involves natural circulation or combined, with the possibility of switching. Closed heating schemes often involve the installation of forced circulation - so they work correctly and are easier to adjust.
So, let's consider the main advantages and disadvantages of both systems.
In the beginning - about merits open system with natural circulation.
- In an open system, the expansion tank performs several functions at once.
- Such a scheme does not require the installation of a safety group, since the pressure can never reach critical values.
- Installation of the expansion tank at the highest point on the supply pipe ensures the spontaneous release of accumulated gas bubbles. Most often - this is quite enough, and installation of additional air vent not required.
- The system is extremely reliable in terms of operation, since it does not contain complex nodes. In fact, the term of its "life" is determined only by the condition of pipes and radiators.
- There is no complete dependence on the supply of power, no electricity is consumed.
- The absence of electromechanical units is the quiet operation of heating.
- Nothing prevents to equip the system forced circulation.
- The system has an interesting property of self-regulation - the intensity of circulation of the coolant depends on the speed of its cooling in the radiators, that is, the air temperature in the rooms. The higher the heating, the lower the flow rate. This often allows you to balance the system without the use of complex adjusting devices.
Now - about her shortcomings:
- The rule of installing the expansion tank at the highest point often leads to the need for its location in the attic. If the attic is cold, then a mandatory reliable thermal insulation of the tank will be required - to prevent serious heat losses and to avoid freezing at low winter temperatures.
- The open tank does not interfere with the contact of the coolant with the atmosphere. And this, in turn, entails two negative points:
- Firstly, the coolant evaporates, so you need to monitor its level. In addition, it restricts the owners in choosing the coolant - evaporation of the antifreeze entails certain material costs. Moreover, the concentration of chemical constituents may change, and for some boilers (for example, electrolytic ones) this is unacceptable.
- Secondly, the liquid is constantly saturated with oxygen from the air. This leads to activation of corrosion processes (steel and aluminum radiators are especially affected). And the second negative - increased gas formation during heating.

Aluminum radiators for open heating systems are of little use
- Such a system causes certain difficulties in the installation - it is required to maintain the required level of slope. In addition, pipes of different diameters, including large ones, will be required, since for each section with natural circulation it is necessary to observe the required cross-section. This circumstance also complicates the installation and leads to significant material costs, especially when using metal pipes.
- The possibilities of such a system are very limited - if the distance from the boiler is too far from the boiler, the hydraulic resistance of the pipes may be higher than the created natural liquid head, and circulation becomes impossible. By the way, this completely excludes the possibility of using "warm floors" without special additional equipment.
- The system is very inert, especially during the "cold start". A serious initial "impulse" is required, that is, starting to a detachment to a higher power to ensure the beginning of the circulation of the liquid. For the same reasons - there are certain difficulties in fine balancing of the system by floors and rooms.
And now take a look at the closed system with forced circulation.
Her dignity:
- Given the correct selection of the circulation pump, the system is not limited to either the storey of the building or the size of the plan.
- Forced circulation provides faster and uniform heating of the radiators during start-up. It is much easier to give subtle adjustments.
- There is no evaporation of the coolant and its saturation with oxygen. There are no restrictions either on the type of liquid or on the kind of radiators.
- The tightness of the system prevents air from entering the pipes and radiators. Gaseous formation in a fluid gradually vanishes, and is easily eliminated air vent.
- It is possible to use pipes of smaller diameter. When installing them, no slope is required.
- The expansion tank can be installed in any place convenient for the owners in a heated room - the possibility of freezing is completely excluded.
- The difference in temperature at the outlet from the boiler and in the "return" with stable operation of heating is much less. This circumstance considerably increases the service life of the equipment.
- Such a system is the most flexible in terms of the use of heating appliances. It is suitable for "classical" radiators, for convectors and "heat curtains", wall or concealed, and for "warm floor" contours.
Disadvantages a little, but they still are:
- For correct operation it will be necessary to perform a preliminary calculation of all components of the system - the boiler, radiators, circulation pump, expansion tank, in order to achieve full consistency of their operation.
- It is impossible to do without installing a "security group".
- Perhaps the most important drawback is the dependence on the stability of the electric power supply.

Most likely, this will require the purchase and installation of uninterruptible power supplies (if the design does not imply the possibility of switching to natural circulation with a non-volatile boiler).
Circuit diagrams in a two-story house
How to build a heating pipe in a two-story house? There are several schemes, from the simplest to the most complex.
First of all, you need to decide whether the system will be one pipe or two pipe.
- An example of a single-pipe system is shown in the figure below:

One-pipe system - the most imperfect
Heating radiators are as if "strung" on one pipe, which is looped from the outlet to the entrance to the boiler and through which both the supply and the removal of the coolant are carried out. The obvious advantages of this scheme are its simplicity and minimum consumption of materials during installation. To this, alas, her dignity ends.
It is quite obvious that the temperature of the liquid drops from the radiator to the radiator. Thus, in the rooms located closer to the boiler room, the temperature of the batteries will be substantially higher than in the rooms located further down. Of course, this can be compensated to some extent by a different number of heating sections, but this is only seen in small houses. If we consider that this article is about a two-story building, then such a scheme is unlikely to be the best solution.
Part of the problem is solved when installing a single-pipe system - "Leningrad", the scheme of which is shown in the figure below. The input and output of each battery in this case are interconnected by a bypass-bypass, and heat losses as far as the distance from the boiler are no longer so significant.

The "Leningrad" scheme allows you to eliminate some of the problems
"Leningradka" lends itself to even more modernization. So, on the bypass it is possible to establish an adjusting valve. The same valves can be installed on one or even both radiator connections (shown by arrows). This immediately opens up wide possibilities in more fine tuning of the heating system for each room separately. There is access to each radiator - it can, if necessary, simply turn it off or remove it for replacement, without disturbing the performance of the entire circuit.

Improved "Leningrad" with shut-off and balancing valves
By the way, its flexibility, simplicity, low consumption of pipes, "Leningrad" has gained immense popularity - it can often be found in single-story houses (especially with a pronounced perimeter of the walls), and in high-rise buildings. It is also suitable for a two-story mansion.
Nevertheless, it is not without its drawbacks. Completely excluded the possibility of connecting to it the contours of the warm floor, heated towel rails, etc. In addition, the relative location of rooms, doors, exits to balconies and m.. not always allow to stretch the pipes along the entire perimeter, and the "Leningrad" in the final analysis should be a closed ring.
- Two-pipe heating system - much more perfect. Although it will require more material consumption and it will be more difficult to install, but it's more preferable to stay on it.
As a matter of fact, it imposes parallel feed pipes and "returns" running parallel to each other. Radiators in this case are connected by branch pipes with each of them. An example is shown in the diagram:

Radiators are connected to feed pipes and return pipes in parallel, and each of them does not affect the operation of others in any way. Each "point" can be adjusted very accurately individually - for this purpose, use bypass-jumpers (item 1), on which it is possible to install balancing valves (item 2) or even three-way control valves (item 3), constantly maintaining a stable temperature heating a particular battery.
The advantages of a two-pipe system are undeniable:
- The total heating temperature at the inlet to all radiators is maintained.
- The total loss of pressure from the hydraulic resistance of the pipes is substantially reduced. This means that you can install a smaller pump.
- Any of the radiators can be turned off or even removed for repair or replacement - this will not have an effect on the system as a whole.
- The system is very versatile, and it is possible to connect to it any heat exchange devices - radiators, warm floors (through special collector cabinets), convectors, fan coil units, etc.
Perhaps the only drawback of the two-pipe system is its material consumption and the complexity of installation. In addition, calculations for its design will also increase.
One of the complex but very effective versions of the two-pipe system is the collector or beam distribution. In this case, from two collectors - feed and return, to each radiator two individual pipes are stretched. This certainly, many times complicates the installation - and the material will be required incomparably more, and to hide the collector wiring is heavier (usually it is placed under the floor surface). But the adjustment of such a scheme is highly accurate, and can be carried out from one place - from a collector cabinet equipped with all necessary adjusting and safety equipment.
By the way, on the scale of a two-storey building, it is often necessary to resort to a combination of connection schemes, two-pipe and one-pipe, in certain areas, where it is more profitable and easier from the viewpoint of installation, and does not affect the overall efficiency of heating.

The next important issue is the flooring of pipes.
There are two main options. The first is a system of vertical risers, each of which provides heat to both floors simultaneously. And the second - a scheme with the so-called horizontal risers (or rather they will be called "sunbeds"), in which each floor has its own wiring.
An example of wiring with risers is shown in the figure:

In this version, risers with lower wiring. From the horizontal sunbeds of the first floor are understood upward mp of the inflow, and here return "returns". In this case, in the upper extremity of each riser, air vent.
There is another option - risers with a top feed. In this case, the outlet pipe of their boiler immediately feeds rises, already on the second floor or even in the upper technical room, vertical risers are connected to it, piercing the structure from top to bottom.
The scheme with risers is convenient in the event that the floor layout is largely identical, and the radiators are located one above the other. In addition, this option will be optimal when the decision is made yet to apply open system heating with natural circulation - in this case the most important task is to minimize the extent of horizontal (inclined) sections, and the risers do not have a serious resistance to the flow of the coolant from the top down.
An example of such a system is shown in the following diagram:

From the boiler (item 1), a common large diameter supply pipe is lifted, which enters the large expansion tank (key 3), located at the top of the system approximately centrally between the risers. The solution is quite interesting - the expansion tank simultaneously plays the role of a kind of collector, from which the supply pipes to vertical risers run out in all directions. To the risers are connected radiators of both floors (item 4), the exact adjustment of which is carried out by special valves (item 5).
As already mentioned, systems with natural circulation are quite demanding for an accurate selection of conditional pipe diameters. On the diagram these are shown by letter designations:
a-dy = 65 mm
b - dy = 50 mm
c - dy = 32 mm
d - dy = 25 mm
e - dy = 20 mm
The disadvantage of the system with the risers is considered to be quite a complicated implementation of it - you will have to organize several inter-floor transitions through the overlap. In addition, vertical risers are almost impossible to "remove from the eyes" - this is important for those owners who have decorative finishing rooms in priority.
An example of a two-pipe system with individual wiring for each floor is shown in the following diagram:

Here - only two vertical risers located nearby - for filing and for "return". This principle looks quite rational from the point of view of installation, it allows completely to disconnect the whole floor in case it is temporarily not used for some reason. In addition, the pipe installation allows almost completely concealing them from view, covering with a floor covering and leaving only the inlet and outlet pipes for the radiators.
In fact, on each floor can be used its own scheme, depending on the layout of the rooms. There are many options for the location of pipes and the connection of radiators with floor wiring. Some of them are shown in the diagram, where the conditional division into three floors is carried out.

- Conditional ground floor - simple double-tube wiring of "dead-end" type with counter motion of coolant is applied. The scheme has its own characteristics. Feed and return pipes are mounted parallel to each other to the very end of the branch (there can be several branches - two are shown on the diagram). The diameter of the tube gradually narrows from the radiator to the radiator. It is very important to provide balancing valves, otherwise the radiators installed closer to the boiler are able to close the coolant flow through itself, leaving the subsequent points of heat transfer unheated.
- The second floor shows the so-called "loop"Tikhelmana". A very successful scheme in which the flows in the feed and the "return" go in one direction. Diagonal connection of the batteries is provided - the input from above and the output from below - this is considered optimal from the point of view of heat transfer. Very often, this scheme does not even require the balancing of the radiators. But there is an important condition - pipes must be of the same diameter.
- The third floor is equipped according to the already mentioned collector scheme. From two collectors there is an individual wiring to each radiator with pipes of strictly one diameter. The system is the most convenient in fine tuning. It should be used if installation of "warm floor" contours is planned. It is desirable that the collectors are located as close to the center of the floor as possible - to maintain an approximate proportionality of the lengths of all "rays" departing from them.
There are many other variants of two-story house, and all of them will not be considered on the scale of one article. In addition, much depends on the "geometry", the architectural features of the house, and to develop "universal recipes" - simply impossible. In such matters it is better to trust experienced experts - they will help to choose the right scheme for specific conditions.
Video: useful information on radiator heating circuits
Basics of calculating the main elements of the heating system
It is not enough to decide on the type of heating system and the layout of pipes - it is necessary to clearly define the operational parameters in order to correctly purchase and install the basic necessary elements - heating boiler, heating radiators, expansion tank, circulating pump.
How to calculate the required boiler output?
There are many methods for calculating this indicator. Very often it is possible to meet recommendations to proceed from the total area of heated premises in the house, and then perform calculations at the rate of 100 W per 1 m².
Such a recommendation has the right to life, and can give a general idea of the required heat output. However, it is more suitable for very average conditions, and does not take into account a number of important features that directly affect heat loss at home. Therefore, it is better not to be too lazy, and to make a calculation more carefully.
It is best to proceed as follows. To begin with, draw a table in which all the rooms where the heating appliances will be installed will be listed step by step. For example, it might look like this:
| The room | Area, m² | External walls, number, are included in: | Number, type and size of windows | External doors (on the street or on the balcony) | Calculation result, kW |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TOTAL | 22.4 kW | ||||
| 1st floor | |||||
| Kitchen | 9 | 1, South | 2, double glazed windows, 1,1 × 0,9 m | 1 | 1.31 |
| Entrance hall | 5 | 1, 10-W | - | 1 | 0.68 |
| Canteen | 18 | 2, C, B | 2, double glazed windows, 1.4 × 1.0 | no | 2.4 |
| … | … | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| 2nd floor | |||||
| Children's | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| Bedroom 1 | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| Bedroom 2 | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| … | … | ... | ... | ... | ... |
Having a plan of the house before your eyes and having information about the peculiarities of your housing, walking along it, if necessary, with a tape measure, it will be quite easy to collect all the necessary data for calculations.
Then it remains to sit down for calculations. But we will not bother readers with a long formula and tables of coefficients. In a nutshell, the calculation is carried out based on their already mentioned standard of 100 W / m². But at the same time, many corrections are taken into account, which affect the required capacity of the heating system to maintain a comfortable temperature and compensate for heat losses. All of these correction factors are included in the calculator offered to you - you just need to enter the requested data and get the result.
Calculator for calculating the required heat output of the heating boiler
The calculation is carried out for each room separately and the result fits into the table. And then it remains only to find the amount - this will be the minimum heat output that the heating boiler should give. Naturally, when choosing a model, you can also lay a "reserve", about 20%.
Make sure that the calculator will take very little time!
Comfortable living in a private two-story house depends entirely on the complex of communications, among which one of the main places is the heating network. It is responsible for maintaining the optimum temperature regime, minimizing heat losses, and preserving the building itself. Let's try to understand how the heating system functions two storey house and what layout schemes are recognized as the most effective.
It is rather difficult to independently choose the equipment necessary for assembling the heating system. To do this, you need to have special engineering knowledge, be able to calculate heat loss, be guided in detailed calculations and nuances of installation. We recommend that you turn to professional heat engineers, who, as a result of preliminary calculations, will select optimal scheme heating.
If you have the appropriate education or you already have experience in the arrangement of heating in a two-story house, you can choose the heating scheme option yourself, using useful information and skills.
Choice of the source of thermal energy
The heart of the heating network is a heat generator that heats the coolant to the optimum temperature and, if its technical capabilities permit, maintains the specified parameters around the clock.
A wall-mounted gas boiler with a capacity of 28 kW with two independent circuits, a closed combustion chamber and convenient electronic ignition is an excellent option for a 2- or 3-storey building
Among modern sources of heat in private two-story houses use almost everything, sometimes combine 2-3 types. Possible types of heat generators:
- heating boilers;
- infrared emitters;
- ovens (Russian, Dutch, Canadian);
- fireplaces;
- solar collectors, heat pump installations and other types of alternative equipment.
Actively used are heating boilers, which can be classified by type of fuel:
- liquid or solid fuel;
- gas;
- electric.
The second and third options are more economical, and if the house is supplied with gas or electricity, then it is better to choose them.

Sequence of operation of the electric boiler: the heat carrier is heated to the user-set temperature, the pipeline moves to the radiators located on two floors, partially cooled and, under the action of the circulation pump, is sent back to the boiler (+)
If the cottage is built on a non-gasified area, the electric boiler becomes the main one, and as a reserve, a spare source use a fireplace or infrared heating.

The diagram shows the advantage of an infrared heating system: IR radiation provides a comfortable temperature in the lower part of the room, with a convective heating method, on the contrary, warm air always rises to the ceiling
The use of alternative heat generators is largely dependent on the climatic conditions of the region, in addition, a minimum set of relatively expensive equipment (for example, solar collectors) will pay off in at least 3 years.
Which coolant is better
The heat generated by a gas boiler or other heat generator, itself can not spread throughout the premises. For this purpose, a coolant is needed - a substance that freely travels through the pipes and possesses the necessary technical characteristics.
There are technologies for using heated air, especially those in homes with stove, fireplace or electric heating. But, unfortunately, to ensure effective functioning, he has insufficient parameters for heat capacity, density and heat transfer.

Layout of the air heating system in a two-story residential building. Arrows indicate the movement of cold and warm air, which provide ventilation and air conditioning (+)
In contrast to gaseous, liquid substances have an excellent ability to absorb heat, give it away and some time to keep the set temperature. In this sense, the ideal "conductor" is ordinary water. When heated, it fills the pipes and radiators, gradually giving away heat to the living quarters, and the circulation ensures the constancy of the process.
For houses with permanent residence, optimal systems with water as a coolant. To ensure that the heating equipment lasts longer without repairs, and the pipeline is not covered with plaque, the water is run through the filters and enriched with special additives and inhibitors.

Non-freezing antifreeze HotPoint 65 is used in heating and air conditioning systems, designed for 10 heating seasons or 5 years of continuous operation
If the house is a temporary haven or serves as a resting place on weekends, it is better to use antifreeze instead of water. It is a liquid solution with a chemical composition, one of the components of which is propylene glycol or ethylene glycol. Chemicals hinder the freezing of the coolant even during the freezing of the building and constantly maintain the functionality of the network in the operating mode.
Convector and radiator heating of premises
When drawing up a heating project for a two-story or three-story house, radiators and convectors can be used as heating devices.
Radiators, or radiators, are most often equipped with centralized systems. They have a combined operating principle: they transmit thermal radiation and heat the air, which circulates around and passes through the "ribs" of products. They are considered the best option for equipping a two-story private house.

Bimetallic radiators Global Style Extra sectional type are made of steel (internal design) and aluminum (external frame), working pressure is 35 atm
Convectors have a more open design, they consist of copper pipes and heat exchangers. The air enters the heat exchangers, heats up, rises, releasing the place of a new portion of still not heated air. From cooling the device is protected by a volumetric casing.

The principle of the convector equipment: heating the room using natural air circulation. One standard instrument is able to maintain a comfortable room temperature of up to 20 m²
In heating schemes of two-story houses radiators are often used, the choice of which is great due to the variety of structures, sizes and shapes.
Short description of household radiators
All types of home heating radiators can be classified according to the material from which they are made. Modern models of heating appliances produce from the following metals:
- cast iron;
- aluminum;
- steel.

Cast-iron radiator for heating the living room, made in retro style. The metal surface is covered with a heat-resistant paint and painted with floral ornamentation
Previously, sectional radiators of cast iron were distributed, and they can now be found on sale. Cast iron is valued for its wear resistance and its low requirements for the characteristics of the coolant, however, heavy weight is considered a minus. Weight should be taken into account if the project involves installing a radiator on a light wall.
Sectional, that is, prefabricated, models are made from aluminum. They differ light weight and aesthetic appearance, but do not contact with copper parts and react negatively to some types of coolant.

Radiators of heating from aluminum Royal Termo Revolution are ideal for private systems. The special shape of the sections ensures maximum heat transfer. The cost of 1 section is 500 rubles.
Steel radiators are panel, made of pieces of sheet steel, and sectional, consisting of several modules. The first option is considered more reliable due to a simple two-way threaded connection. Steel perfectly tolerates any coolant, it is lighter in weight than cast iron, but heavier than aluminum.
For a two-story house, any type of radiator is suitable, when choosing it is necessary to focus on the type of coolant, the features of the installation of the system and the design of the interior.
The effectiveness of circuits with forced circulation
The prevailing part of modern heating systems can function fully only when creating artificial circulation, that is, in which the coolant moves inside the network due to the operation of the circulation pump.

The scheme of the heating system with a gas boiler in a 2-storey house: the equipment and meters are installed on the first floor (in the basement, in the basement), in a specially equipped room with good noise insulation (+)
For the device of forced circulation in a building with several floors there are prerequisites:
- installation of a pipeline of smaller diameter, which facilitates the assembly of the wiring as a whole;
- provision of zone adjustment (alongside or instead of general);
- the presence of the second and higher floors does not affect the efficiency of heating;
- decrease in the temperature of the coolant without changes in the heat transfer parameters;
- the possibility of using inexpensive plastic pipes.
The disadvantages include the presence of power - there may be interruptions, but they can easily be avoided by using redundant UPSs. The problem of louder noise is also solved by laying the noise insulation layer in the boiler room.

Scheme of water heating with forced circulation: 1 - gas or electric boiler; 2 - riser; 3 - pipe to the expansion tank; 4 - riser for drainage; 5 - upper horizontal wiring; 6 - expansion tank; 7 - circulation pump; 8 - return line
Most appropriate place casing of the circulation pump where the temperature is reduced to a minimum, that is, immediately before the boiler, on the return line.
Natural circulation as an alternative
Now, autonomous heating networks with gravitational circulation, that is, acting according to natural physical laws, can be met extremely rarely. The principle of operation is explained by the difference in the density of cold and heated water and the presence of an additional monitoring device - an expansion tank, which is installed in the upper part of the riser with hot water.

The scheme of the heating system in a two-story house with natural circulation: the upper riser crosses both floors and ends in the attic, near the expansion tank, and the lower contour is located in the basement or on the ground floor (+)
A peculiarity of the natural type network is the inclined arrangement of horizontal pipes (return and distributing) and the location of the boiler - it is set at the lowest possible level. The coolant is supplied through an expansion riser, the discharge of cooled water (or antifreeze) through the return pipe.
Advantages of the gravity scheme are independence from electric power supply, ease of installation, no noise produced circulation pump.
Features of single-pipe heating system
The choice of single- or double-tube heating does not depend on the number of floors in the house - both are suitable, but for buildings with 2 or more floors the installation of a circulation pump is mandatory. The most effective is heating with a liquid coolant (water or antifreeze), whereas for small single-storey houses, for example, summer cottages, you can consider other options.
Principle of operation and distinguishing features
Heating radiators, according to a single-pipe scheme, are connected in series, that is, the heat carrier first falls into one device, the one nearest to the boiler, from it through the pipeline to another, etc. The ringed contour, which is a network, is also suitable for a 2-storey house, since it is conveniently located along the walls along the perimeter.

The simplest scheme of single-pipe heating for a 2-storey building: from the supply pipe, the heating medium enters the heating radiators connected in a sequential order
The presence of shut-off valves can improve the use of the system. For example, the Maevsky crane is designed to remove air "traffic jams" that often occur during idle time, that is, in the summer. In addition, various models of balancing valves, ball valves, special regulators are used.
Forced circulation in a single-tube design with a temporary lack of electricity can be replaced by a natural one, but this requires the installation of a membrane tank and the location of horizontal pipes at an inclination of up to 5 °.
Assessment of shortcomings and advantages
The main advantage of single-pipe networks is considered to be an easier design and installation itself. The minimum of pipes allows not to be guided by a complex lay-out of premises, but simply to lay the pipeline strictly along the perimeters of both floors. The savings in the purchase of fewer elements - pipes, cranes - are also valued.
One pipe takes up much less space than two, so it can be disguised under a floor covering, invisibly paved in the doorways, that is, to mount without disturbing the interior.

One of the main disadvantages of a single-pipe system, which is relevant for a house with 2 floors, is the rapid cooling of the coolant during successive movement through the radiators (+)
The disadvantages include the need to purchase a more powerful electric pump, which increases the payment for electricity. Adjust the temperature level in the design with consecutive connection more difficult: with a decrease in the intensity of heating in the nearest radiator, there will automatically be a drop in temperature throughout the entire highway.
Common Connection Options
If you decide to equip a single-pipe system, you will have to choose between two types:
- simple scheme without regulation;
- "Leningrad" with the possibility of switching off individual radiators.
By the way of management, the first option is clearly inferior to the second, its only plus - the budget value.

The installation of a simple single-tube system of horizontal or vertical type is simple and reliable, but it is not possible to adjust the temperature in the network (+)
The installation of "Leningrad" will cost a little more, since in addition to pipes it is necessary to purchase a set of stopcocks. With the help of bypasses and valves, it is possible to reduce / increase the amount of coolant supplied to the radiator.

Scheme of the device "Leningradka": with the help of stop valves it is possible to temporarily disconnect some unnecessary radiators without changing the functional qualities of the whole system (+)
"Leningradka" is recognized as professional heat engineers the best option one-pipe system for a 2-storey residential building.
Assembly and installation of equipment
Standard equipment for system assembly:
- circulation pump;
- gas or electric boiler (capacity depends on the size of the house, the characteristics of the coolant, etc.);
- expansion tank;
- pipes 20 mm and 25 mm;
- adapters, gaskets, plugs;
- a set of radiators;
- cranes of Majewski.
Along with steel pipes, polymeric or metal-plastic ones can be used, the latter being preferred.

In heating circuits with closed expansion tanks, air bleeding is performed by means of automatic descenders equipped with shut-off valves and floats, or Maevsky cranes supplying each radiator
First find a suitable place for the boiler and mount it, then collect the pipeline leading to the radiators. In places of radiator branches and bypasses fix tees. The pump is cut into the return, next to the inlet to the boiler, and connected to the power supply.
The place of installation of the open expansion tank is the highest point of the system, the closed one can be mounted in any convenient place, for example, in the boiler room. Radiators are suspended to the walls by means of special fasteners, they are equipped with plugs and cranes.
Two-pipe heating system for a 2-storey building
A truly comfortable living conditions can be achieved only with the installation of a two-pipe heating system. Its design allows you to adjust the temperature in individual rooms and save energy resources.
How does the scheme with two trunks work?
In contrast to the single-tube scheme, the two-pipe system consists of a pair of highways with different purposes: one of them supplies a coolant, the other outputs it back. The radiators are not connected in series but in parallel. One circuit, with a heated coolant, departs from the riser to the radiators of both floors, the second one is mounted to the boiler outlet and is also diverted to both floors.
Radiators are equipped with thermostatic valves, allowing you to set a comfortable temperature. If desired, you can reduce the intensity of heating partially or completely block the flow of water into the device.

Part of the devices are basically cut into the return, for example, before the boiler is traditionally mounted membrane tank, pressure control, circulation pump and safety valve
In modern 2-storey buildings, two-pipe structures are used, since they are much more efficient than single-tube structures:
- reduce pressure loss;
- do not require a powerful pump;
- keep coolant temperature equal for each radiator;
- allow the use of many different thermal devices inside the same system (for example, radiators, convectors and "warm floor");
- enable to repair and replace parts without compromising the overall functionality.
The main disadvantage is the complexity self-installation - During the assembly, consultation and supervision of professionals are mandatory.
Successful solutions for a two-pipe system
There are many implementations of a variety of schemes, but when drawing up a project, one must build on individual requirements.
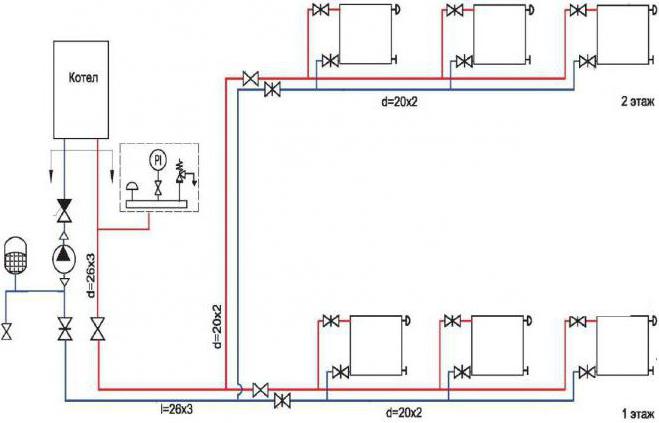
The simplest scheme for the arrangement of a heating system in a 2-storey house. It is characterized by the following items: 2 circuits for heating and hot water production, liquid coolant, forced circulation (+)
A number of universal circuits are suitable for providing heat to houses of different size and number of storeys.
Detailed scheme of two-pipe wiring for a single-storey house with a fully equipped basement floor. The problem of thermal insulation of the floor in the basement is solved by the connection of the water system "warm floor" (+)
If you install additional equipment, for example a membrane tank, the capabilities of the heating system will expand.

A and B are two variants of the wiring device, upper and lower type. Additional equipment: expansion tank, Mayevsky cranes, air line (+)
The following scheme combines the three most demanded wiring diagrams.

1 level - deadlock wiring with parallel installation of both circuits; 2 level - counter wiring, characterized by two-way radiator connection; 3 - collector wiring with improved balancing
All these schemes are suitable for heating a 2-storey building.
Video about heating for two or more floors
Information videos will expand your knowledge of the heating systems of 2- and 3-storey houses.
The scheme of connection of a two-circuit radiator heating system with "warm floors":
The option of wiring the heating system in a 3-storey house (using the "Leningrad"):
Practical application of the system with natural coolant circulation (on a solid fuel boiler):
Thus, the most effective are two-tube heating systems with a liquid heat carrier, equipped with a gas or electric boiler and a circulation pump. Combined systems are more efficient, the selection of heat sources depends on the number of storeys and the design of the house.
In any case, for the creation of an individual scheme, we recommend consulting with a specialist in heating engineering.
The heating system is the most important engineering system of life support for any home. Its purpose is to compensate for heat loss and create a certain temperature regime, which is necessary primarily for people living in the house, but do not underestimate the fact that effective system heating is designed to ensure, including, the durability and durability of building structures.
Calculation and design is best entrusted to heat engineers who will estimate the heat loss, give recommendations on the insulation of the house, and also make a detailed calculation that will avoid unnecessary costs for expensive equipment. But the choice of the heating scheme for a two-story house can be made by the customer himself, based on many years of experience in the operation of various systems.
Kinds of sources of thermal energy - heat generators
Before choosing one or another heating scheme, it is useful to know already existing species and which one is suitable for a specific task. It is known that the main source of heat are different types of heat generators, which can be:
- Furnaces and fireplaces. This kind of heating was once the main one, but now it is used less and less because of the high cost of fuel (firewood and coal) and the inability to effectively manage the temperature in the house. In some regions where there is no gas supply, this kind of heating is an uncontested option.
- Various types of heating boilers, which can be: gas, solid fuel, liquid fuel, electric, - depending on the availability of access to various energy sources and their cost.
- Alternative energy sources. This category includes: geothermal energy received by heat pumps, as well as solar, which is converted into thermal solar collectors. This type of heating is in a stage of rapid development and is still used in our country quite rarely because of high prices for equipment.
Perspective of the future - non-volatile houses
- Infrared heating. The sources of heat are special infrared emitters, which are used in most cases electric power. Thermal energy at such heating it is delivered directly to the "addressee" by radiation. For heating large rooms or premises with a low periodicity of the appearance of people in them infrared heating will be an excellent choice.
In some situations it will be reasonable to combine different types of heat generators for heating. For example, if there is a holiday home, where the family comes only for the weekend. In this case, it would be prudent to have a gas boiler for basic heating and electric - to prevent the water from freezing in the winter in the system and to maintain the minimum allowable temperature in the house.
Types of coolants
Any heating system must transfer the heat concentrated in the heat generator before heat device, which heats a concrete room. This is done with a coolant, which can be:
- Air, which is used for heating stoves, fireplaces, as well as various electric heaters. In view of the fact that air has a low density, heat capacity and heat transfer coefficient, it is much inferior to liquid coolants.
- Water is an almost ideal heat carrier because it has a high heat capacity, density, heat transfer coefficient, and chemical inertness. The water heated by the heating boiler is transported to the heat devices by means of a piping system.
In most modern heating systems, water or various antifreezes, being aqueous solutions of ethylene glycol, propylene glycol or combinations thereof, are used as the coolant. Such property as frost resistance at low temperatures can be useful in heating systems of such houses where people are not planned to stay permanently in the winter. In those houses where heating will work all winter, the use of antifreezes is economically inexpedient.
Various antifreezes badly "get along" with aluminum radiators, some seals and pipes. In addition, coolants containing ethylene glycol are poisonous. Therefore, it is necessary to use such compounds only in cases when one can not do without them ..
Types of heating appliances
Heating appliances can be divided into two main classes:
- Radiators - translated from Latin, they are translated as "emitter", that is, an instrument that transmits heat in the form of infrared heat radiation. However, modern radiators are not purely radiators, but still transmit some of the heat in the form of convection, but they retain their name.
- Convectors - the transfer of heat energy to the room is due to heating the air, and he already gives it to all surrounding objects. Such heaters have copper (less often steel) tubes surrounded by finned heat exchangers. Air, getting into the heat exchanger, is heated by its plates and rises, giving way to a colder one. In order for the air exchange to be effective, the whole convector construction is placed in a special casing.
In modern systems, a heating method such as "warm floor" or "warm walls" is widely used, which in their essence is a large radiator that transmits the "lion's share" of heat in the form of radiation, and this increases the comfort and allows to reduce the temperature of the air in the room approximately 2 degrees, which leads to a fuel economy of about 12%.
Types of radiators
In the heating system of a two-story house can be used perfectly different types radiators, depending on the tasks to be performed, the area of the room, design data, preferences. Radiators can be divided into several types:
- Cast-iron sectional radiators are those we used to see in apartments and houses of old construction. They have a large mass and high thermal inertia, but they are undemanding to the quality of the coolant, are not subject to corrosion, have high heat transfer. Such radiators perfectly fit into any interior, especially classic.
Cast-iron sectional radiators - timeless classics
- Aluminum sectional radiators are an excellent choice for autonomous heating systems, but they are more sensitive to the quality of the coolant, do not tolerate direct contact with copper pipes. Such radiators perfectly fit into any interiors.
- Bimetallic sectional radiators are a combination of steel or copper pipes, through which the coolant circulates and an aluminum surface that transfers heat to the room. Such radiators are undemanding to heat carrier, withstand high working pressure, outwardly practically indistinguishable from aluminum ones.
- Steel panel radiators - this is a one-piece construction from stamped and welded sheet steel. Such radiators have only two threaded connections to the heating system, which increases their reliability. High heat dissipation, low weight, low inertia, aesthetic appearance - all this made them the most popular in autonomous closed systems heating houses.
In addition to these models, manufacturers still produce various design models, which include solid cast iron, steel tubular and even ceramic. The high price for these devices is due to the fact that the design ambitions in them predominate over engineering rationality.
Heating schemes for a two-story house
The number of realizations of the heating system of a two-story house is infinite, since it depends on many factors: the size of the house, the availability of uninterrupted power supply, the permanence of living in people's homes, etc. Therefore, it will be reasonable to consider several typical schemes that have proven effective.
The scheme of heating the house with natural circulation
The name of such a system speaks for itself - the circulation of the coolant in the heating system is due to natural processes. The work of such a system can be considered in the figure.
The water heated in the heat exchanger of the boiler decreases in density and is displaced by the colder and denser water of their return line. It is this difference in the balance of hot and chilled water that provides circulation in the heating system. At the uppermost point of the hot water stand, an expansion tank is installed that allows the water to expand when heated, allows you to monitor the water level in the system and, if necessary, make water. In addition, all the air that will inevitably be present in the system will go into the expansion tank.
Diluting pipelines and return lines, called loungers, are always made under the slopes to facilitate water circulation: the upper deck bed to the radiators, and the lower one to the boiler. In such a system, the boiler must be at the lowest point. The flow of coolant to the radiators is done through the hot water risers, and the drain is cooled through the return risers.
One of the options for implementing a two-pipe heating system of a two-story house with natural circulation is presented in the following scheme.
It should be noted in this scheme for a large number of pipelines and their high conditional pass - dy. This is due to the fact that in the gravity systems, to ensure circulation of the heat carrier, it is necessary to minimize the resistance, and this is only possible in pipes of large diameters.
Systems with natural circulation, of course, have advantages:
- Independence from power supply - the heating system will work both in the total absence of electricity, and during interruptions in its supply.
- The reliability and simplicity proved by long years of operation.
- Absence of pumps and low circulation speed of the coolant make such a system noiseless.
Despite all the advantages, such systems are gradually disappearing into the past, as they no longer meet modern requirements for heating systems.
- Gravitational systems are extremely material-intensive - large-diameter steel pipes are used for their installation.
- Installation of heating systems with steel pipes is technologically complicated and takes a long time.
- Systems with natural circulation have restrictions on the area of heated premises. According to the experts, the total length of the horizontal sections (sunbeds) should not exceed 40 meters, and the total area of 150 m2.
- High inertia - from the moment of starting the system to heating up all the radiators to the design temperature, it can take several hours.
- A large difference in the flow and return temperature can adversely affect the boiler's heat exchanger.
- In the coolant of gravity systems, a large amount of dissolved oxygen, which affects the corrosion of pipes and radiators, therefore, in such systems only cast iron or bimetallic radiators can be used.
Heating systems with forced circulation
Almost all modern systems heating use only forced (artificial) circulation of the coolant, which gives significant advantages.
A secondary heating systems, which are used in private houses, have undoubted advantages over centralized systems: they are manageable and economical. Only owners of private houses can independently adjust the intensity of heating, connect additional circuits and install the type of radiators that they like. The scheme of heating a 2-storey private house must meet not only operational requirements, but also be trouble-free, economical, simple and durable.
Scheme of heating a private house
The choice of heating scheme is mainly influenced by the area of heated premises, that is, the total length of the pipeline. The main task of any heating system is the uniform heating of the premises throughout the entire length of the pipeline. If it is not difficult to organize such a system, then in cottages with two levels, serious calculations must be made to solve the same problem.
Any heating system consists of the main elements:
Video: scheme of heating two-story house
Systems with installation of a circulation pump
Any scheme of heating a 2-storey private house should ensure a constant circulation of the coolant through the system. In this case, the efficiency and speed of heating the rooms directly depends on the level of hydraulic pressure in the pipes. Obviously, the simplest solution to this problem is.
Pump circuits are good in that by means of a small and economical pump the system provides the preset pressure, and hot water will be delivered to any point of the circuit regardless of its location. The power consumption of such a device is from 25 to 50 watts per hour. Even with daily continuous work per month, the meter will reel not more than 40 kW, which does not significantly affect the flow rate family budget. This scheme has a serious drawback - it does not work in the event of a power failure. Unfortunately, such situations are not uncommon in Russia, so in the winter it is necessary to have at your disposal so as not to remain without heat at all.

Systems based on natural circulation
Knowing the basics of thermodynamics, you can develop such a heating scheme that the pump is not needed. Such a scheme is based on the ability of the heated liquid to rise upward. Located at the level of the first floor, the boiler or stove heats the water, this water rushes upward, triggering the flow of the coolant through the closed-loop system.
In systems without circulation pumps, it is impossible to provide high pressure, because its level depends on the temperature of the liquid. For this reason, systems with natural circulation have their own peculiarities:
- in order to reduce the resistance, the diameter of the pipes should be at least 32 mm, the same applies to the tubes of working radiators;
- the maximum height of the water pipe, through which hot water rises and enters the heating circuit, should not exceed 6 meters, that is, systems with natural circulation can qualitatively heat no more than two floors;
- the wiring diagram should be as simple as possible, but if the length of the pipes is large, it makes sense to make two circuits;
- without using the pump, the system will not work, so its circuit must be connected separately.

Advantages and disadvantages of working schemes
Pumping systems have obvious advantages in the form of a constant operating mode, guaranteeing efficiency and ease of installation. The main drawback is the equipment's volatility. Circuits with natural circulation can be called truly autonomous, but in this way it will be possible to heat a limited area, and the heating process will take much longer. The installation of such systems is a complex and painstaking business, the preliminary calculation must be carried out very accurately.
There are various alternative schemes, among which combined, when one of the circuits is supplied with a circulation pump. These are complex systems that are used in houses of a large area, for a residential two-story house they are rarely expedient.

Types of wiring and calculation methods
For the calculation of heating systems it is necessary to take into account many factors, including:
- the area of the house;
- calculated values of air temperature inside and outside, required humidity;
- materials from which the house is built and the quality of thermal insulation;
- the number of windows and the intensity of natural sunlight.
In accordance with the specified parameters, according to the SNIP tables, the required power can be calculated boiler and the required pressure in the system.
Common Concepts
For small houses in the area of one or two floors, the simplest single-pipe circuits are suitable, which are easy to assemble and calculate, can operate without a pump, but are considered to be the least effective.

The improved scheme - the so-called "Leningrad" - a system in which each radiator is connected in parallel, and the control valves allow more efficient use of heat and redirect hot water.

The principle of the two-pipe system is that the heated water is supplied to all radiators simultaneously, and its temperature is the same at each input. Chilled water is diverted through the return pipe, which is also common.
Related article:
Asked a question,? Read all about their types and selection criteria in a separate publication of our portal.

There are schemes with lower and upper feed. In the first case, water, rising up the riser, supplies first the first floor, and then the second. With the upper system the opposite is true: the heated water rises in a common riser and then fed to the radiators of the upper floors, cooled and returned back.

Schemes with open and closed expansion tank
Expansion tank in heating system plays the role of a regulator of water level, and also insures the system against pressure drops. The expansion tank is usually installed in the coldest place in the system - on the return pipe. It should be located in a heated room to prevent freezing of water in it in the winter.
There are two types of tanks - open and hermetically sealed. Open tanks They are used in circuits with natural circulation, and closed membrane ones only in systems with a pump. Read more about the separate publication of our portal.

How to choose the best scheme
The heating scheme of a small 2-storey private house can be mounted in any of the ways listed above. The question of the application or non-use of the circulation pump is fundamental. More details about the features of each heating circuit can be found in the video below.
Video: heating scheme of a two-storey house heated floor + collector heating
Maybe you will also be interested:
 Antifreeze for the heating system of a country house
Antifreeze for the heating system of a country house  Water supply of a private house from a well: scheme and organization
Water supply of a private house from a well: scheme and organization
In the process of construction and long before laying the foundation, there are many questions related to heating. Each owner wants to achieve positive results, following the path of less resistance.
Scheme with natural circulation
Considering the heating scheme of a private 2-storey building, you can pay attention to a system that involves the natural circulation of water. The choice of the drawing will depend on the layout and area of the building. But this is the most widespread and customary for country houses and country houses. It differs little from the one used in the arrangement of heating systems in single-storey buildings.
When choosing such schemes of heating a private 2-storey building, you should remember the layout features that require the choice of a place for mounting the expansion tank. There is no need to place it in the attic, you can confine yourself to the second floor. There the tank can be anywhere. Of course, this should be the highest point of the room. The master must ensure that the water can be discharged. If you apply this method of devices, the liquid will come from above. Thanks to this, the heating of the radiators will be even, as far as the heated premises are concerned.
In order to direct the movement of water, the pipes are located at a slight angle of 3-5 degrees. The diameter of the return pipeline should increase as it approaches the boiler equipment. If such heating schemes of a private 2-storey building are used, the supply pipeline can be placed under the usual window sills or ceiling.
The advantages of a heating circuit with natural circulation

It is important to consider the merits of the scheme described above before starting the installation work. There are a lot of them. First of all I want to note the reliability of the design. In addition, among the positive aspects should be distinguished ease of operation, noiselessness of operation, independence from the supply of electricity.
Disadvantages of the scheme

If you decide to use the above-mentioned project for heating a 2-story private house, you should also remember the shortcomings, which in this case are much greater than the pluses. First of all, it is worth highlighting the complexity of installation work and the need to lay pipes with a slope. Among other things, the heated area will be small. The system will not have enough pressure to heat the house if its area is more than 130 square meters.
You should also know about the low efficiency and significant temperature difference between the return and feed. The latter circumstance negatively affects the operation of the boiler equipment. The internal surfaces of the system will be corroded, since oxygen will be present in the coolant. Owners of the house need to constantly monitor the state of evaporating water, which implies the need for its addition. As a result, scales can form on the pipes. Use antifreeze is unacceptable for the same reason. As another drawback, it is worth highlighting the significant material consumption of the system.
Types of circuits with forced circulation

Heating private 2 with their own hands can be equipped and the principle of a system that works by forcing water to circulate. According to the professionals, the following schemes are the simplest to install: one-pipe, two-pipe and collector. First, we will analyze the first variety.
with my own hands made

When using this scheme, the movement of the coolant will divide the heating devices into two branches. One of them goes to the first floor, while the other goes to the second floor. On each floor, a stop valve is installed at the inlet of the pipe. It will only heat half the rooms. After the pipes with the coolant pass through the heating devices, they will be combined into one system, which will be suitable for the boiler equipment. To connect the batteries on each floor to be the same method, which is used in the conditions of single-story buildings.

If you have chosen the above scheme of heating a 2-storey private house, the shut-off valve must be installed at the entrance of each heater. This is necessary for adjusting the heating level of the radiator and balancing the system. At the output of the batteries, a shut-off valve is installed, which is used to turn off the radiator during repair and replacement. If you use such a connection scheme, you can change the heating devices without stopping the system and draining the water. To vent the air, a valve is installed on each battery at the top.
This scheme of heating a 2-storey private house involves the installation of batteries with a bypass line. This increases the uniformity of heating the building. You can also install heaters without bypass. In this case, it is necessary to install in the house radiators of different thermal capacity, taking into account the loss of cooling water. This indicates that the farther from the boiler the battery is, the more sections it should have. If you neglect this rule, then in some rooms it will be hot, but in others it's cold.
The scheme of heating without valves

When the heating system of a private 2-storey building is assembled by one's own hands, the shut-off valve can not be used. Rather, it can be used in smaller quantities. However, under such conditions maneuverability will be reduced. In this case, there is no need to talk about separate heating of the second and first floors.
The main advantages and disadvantages of single-pipe heating system
Using such schemes of heating a private 2-storey building, you ensure the ease of installation. Owners of housing at the same time receive effective heat transfer, as well as savings on materials. Among the minuses of the heating scheme, one can distinguish the uneven distribution of heat across the radiators and the need for balancing the system. However, all these drawbacks are completely devoid of a two-pipe system, which works by means of forced circulation of water.
Circuit with forced circulation
A two-pipe system with forced circulation guarantees an even distribution of heat. It is effective and sometimes compared to the circulatory system of man. In it to each radiator the coolant is fed through a branch running from the common supply pipe. The presence of a tap is also envisaged in return pipeline each radiator.
Batteries are installed with air vent and shut-off valves on the supply. This allows you to change the heating level of the heater. In order to increase safety and eliminate excess pressure in the radiator, on the battery tap return pipe The shut-off valve is not installed. Under the sill or ceiling, you can lay a feeding pipe. It is perfectly permissible to equip such heating of a private 2-storey building with one's own hands. The schemes presented in the article will allow you to carry out these works without recourse to specialists.
The main shortcoming of the two-pipe system is the high material intensity. For the return and delivery of the pipe will need a double copy. Among other things, they are difficult to decorate, and hide is not always possible, which spoils the interior of the premises. All of the above shortcomings are completely devoid of a collector circuit.
Description of the collector circuit
Such a system can be successfully used for a single-story or two-story house. It functions due to the forced movement of water, which is previously fed to the collector. Each heater must be connected to the collector through a shut-off valve. In the role of advantages it is worth highlighting the possibility of dismantling and installing radiators on the operating system, with which to drain the coolant and stop it will not have to.
The system is easy to manage. Each circuit is independent and connected to a separate automatic control system with its circulation pump. In a tandem with this heating system, you can use a warm floor. Pipes are laid in a raised floor, and also located in a separate cabinet. This heating of a private 2-storey building can be easily installed by oneself. Schemes, photos of similar drawings can be found in the article.
Recommendations for installing heating appliances in a two-story house
If you want to ensure an even distribution of heat in the home, it is important to correctly calculate the length of the main, take into account the level of insulation of the house, as well as the presence of window and door openings. The efficiency of heating will depend on the proper placement of heating equipment, this primarily applies to radiators. The battery should be located under the window, and the warm air rising above it will block the cold masses from the window. This way you can eliminate cold air. When the heating system of a private 2-storey building is arranged by oneself, it is important to think about such premises as a boiler room, an entrance hall and a corridor. For them, one kilowatt of heat capacity per 10 square meters will suffice.
For the bathroom, kitchen and hall will need 1.2 kilowatt per 10 square meters. For a nursery and a bedroom, the level of thermal capacity should be increased to 1.5 kilowatts per same area. Thermal efficiency will depend on the floors, floor material and walls. In order to reduce costs, as well as to ensure the optimal heating mode in each room, you should use thermal regulators. The battery material will affect the system parameters. Today as the best option there are aluminum batteries. High parameters are distinguished by bimetallic radiators, however, they will have to pay more for them.
If you know that the heating system is low enough water quality, then do not use aluminum radiators, which are most sensitive to aggressive conditions. Rigid or contaminated water will also affect the longevity of the equipment and the operability of the system. But the steel and cast-iron batteries will last much longer. These factors do not have a negative impact on them.
Material of pipelines
The heating system of a 2-storey private house should be equipped using a quality pipeline. Modern technology almost does not use metal pipes, as corrosion processes are the cause of failure of such products. If we take into account that in smaller systems the less pressure of the working fluid is used, it is better to use a plastic pipeline.



