What determines the heat transfer of the radiator. Method for calculating the heat dissipation of the radiator of heating batteries
The question of the effective operation of the heating system depends to a large extent on how the heat output of the radiators is calculated. These devices are the main source of heat, which heats the air inside the premises. Therefore, even at the design stage, engineers conduct calculations, based on which in each room a radiator with a certain number of sections is installed. These calculations are not so simple, because they have to take into account a large number of criteria.
What do you need to consider when calculating?
Calculation of radiators
Be sure to take into account:
- Material from which the heating battery is made.
- Its size.
- Number of windows and doors in the room.
- The material from which the house is built.
- The side of the light in which the apartment or room is located.
- Presence of thermal insulation of the building.
- Type of wiring of the pipe system.
And this is only a small part of what needs to be considered when. Do not forget about the regional location of the house, as well as the average street temperature.
- Normal - using paper, pen and calculator. The calculation formula is known, and it uses the main indicators - the heat output of one section and the area of the heated room. Also, coefficients are added-lowering and raising, which depend on previously described criteria.
- Using the online calculator. This is an easy-to-use computer program in which certain data about the dimensions and design of the house are loaded. It gives a fairly accurate indicator, which is taken as the basis for designing a heating system.
For a common man in the street, either option is not the easiest way to determine the heat output of a heating battery. But there is another method for which a simple formula is used - 1 kW per 10 m² of area. That is, to heat a room of 10 square meters, it will take only 1 kilowatt of thermal energy. Knowing the heat transfer coefficient of one section of the radiator, you can accurately calculate how many sections need to be installed in a particular room.
Let's look at a few examples of how to do this correctly. Different types of radiators have a large size range, which depends on the interaxial distance. This is the size between the axes of the lower and upper collector. For most of the heating batteries, this figure is either 350 mm or 500 mm. There are other parameters, but these are found more often than others.
This is the first. Secondly - in the market there are several types of heating appliances from different metals. Each metal has its own heat transfer, and this must be taken into account in the calculation. By the way, which one to choose and put the radiator in your house, everyone decides for himself.
Heat dissipation of cast-iron radiators
The range of heat transfer of cast-iron batteries varies between 125-150 W. The spread depends on the interaxial distance. Now you can calculate. For example, your room has an area of 18 m². If it is planned to install a 500 mm battery, then we use the following formula: (18: 150) x100 = 12. It turns out that in this room you need to install a 12-section radiator.
It's simple. Similarly, it is possible to calculate a cast iron radiator with a center distance of 350 mm. But this will be only an approximate calculation, because for accuracy it is necessary to take into account the coefficients. They are not so many, but with their help you can get the most accurate figure. For example, the presence of not one but two windows in the room increases the heat loss, so the final result must be multiplied by a factor of 1.1. We will not consider all the coefficients, since this will take a lot of time. We already wrote about them on our website, so find the article and read it.
Heat dissipation of aluminum radiators
For comparison of two opposite metals, an aluminum battery was chosen. Aluminum radiators

Heat dissipation of Global radiators is calculated according to EN-442
the heat output is greater, and one section radiates 200 watts of heat. Substituting this indicator in the formula, we determine how many sections should be used in a room of 18 m².
(18: 200) x100 = 9. The number of sections decreased only due to high heat transfer of aluminum devices. So you can choose a radiator not only in size, but also in the model.
Connection method
Not everyone understands that the distribution of heating pipes and proper connection affect the quality and efficiency of heat transfer. Let us examine this fact in more detail.
There are 4 ways to connect the radiator:
- Lateral. This option is most often used in urban apartments of multi-storey buildings. There are more apartments in the world than private houses, so manufacturers use this type of connection as the nominal method of determining the heat transfer of radiators. To calculate it, the coefficient is 1.0.
- The diagonal. Ideal connection, because the coolant passes through the entire device, evenly distributing heat over its volume. Usually this type is used if there are more than 12 sections in the radiator. The calculation uses an incremental factor of 1.1-1.2.
- Lower. In this case, the supply and return pipes are connected from below the radiator. Usually this option is used for hidden pipe wiring. In this type of connection there is one minus - heat loss of 10%.
- Single pipe. This, in fact, the bottom connection. Usually it is used in the pipe distribution system. And here it was not without heat loss, however, they are several times larger - 30-40%.
Conclusion on the topic
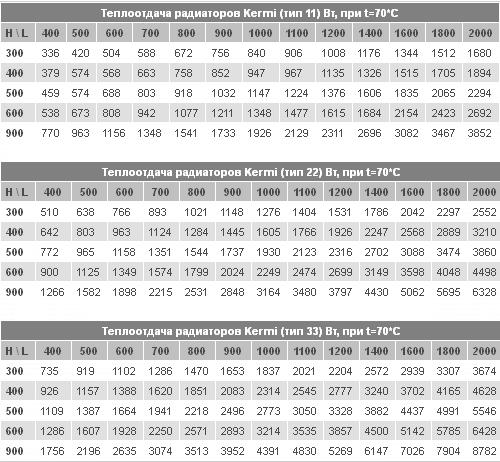
Table of power of radiators
You yourself were able to make sure that it is possible to calculate the heat transfer of the radiator correctly in a simple way, although it is not very accurate. In addition, we have to take into account the wide dispersion of the size parameters of the batteries, the materials from which they are made, plus additional factors. So everything is complicated.
Therefore, we advise you to act simpler. Take for the basis of the very formula with the ratio of the area of the room and the required amount of heat. Make a calculation and add to it up to 10%. If your house is in the northern region, add 20%. Even 10% is very generous, but there is no excess heat. Moreover, it is possible, using various devices, to control the supply of coolant to the radiators. You can reduce, but you can increase. The only disadvantage of this increase is the initial cost of purchasing radiators with a large number of sections. Especially it concerns aluminum and bimetallic devices of heating.
The generally accepted temperature of apartment comfort is considered to be 21 0 Celsius. To have it in the apartment at this level and in winter cold, various heating systems are used, including autonomous and central heating systems. Common sense and competent calculation of the heat dissipation of the radiator of heating batteries allows you to install the required number of heating appliances, including radiators.
Goals and tasks of calculations of radiators of heating
Calculations of radiators are carried out to ensure the effective functioning of the heating system for heating a particular living space, and in calculations thermal comfort is treated not only as a plus temperature of arbitrary magnitude, but also the maximum permissible. It makes no sense to install an extra-high amount of heaters, if you have to open the window for the sake of fresh air (remember, too hot batteries "burn" oxygen). That is, the calculations determine the boundaries of low-temperature and high-temperature heating.
Another task of thermal calculations is to determine heat transfer parameters, which allow to distribute heat flows evenly throughout the room. In this case, heat losses are to be taken into account, depending on the presence in the basement and attic room, such as wall material, wall thickness, window sizes and many other attendant factors.
When designing a building object, special programs are used, thermal imagers can be used to calculate radiators in an apartment. But for rough calculations, simple algorithms are used, which are usually called calculators for calculating heating batteries. Their methods are based, basically, on the ratio of the required heat output of the heater and the area of the heated space.
Method of calculating the radiator by area
In the basis of the conditional calculation for the area, the value of the heating capacity, regulated by sanitary standards, per 1 sq. meter area of the room. For a temperate climate at the latitude of Moscow, this figure is from 50 to 100 watts. For northern areas above 60 0 north latitude it is higher and is accepted in the range from 150 to 200 W per 1 sq. Km. meter. Passport value of heat transfer of one pig-iron section is specified in the size from 125 to 150 W. 
Determine the required power for 15 square meters. meters:
100 x 15 = 1500 watts.
Determine the number of sections:
1500/125 = 12 sections, which can be represented as two six-section cast-iron batteries.
This calculation is also equivalent for a bimetallic radiator, since its heat transfer has practically the same values.
In the calculations, the norms for the ceiling of the standard height of 270 cm were used. For higher ceilings, radiator calculations based on the cubic room parameters are performed.
Method of calculating the radiator by volume
In this case, the technique, or as it is called, the calculator for selecting kw batteries, operates with such concepts as the nominal heat flux Qn of a particular type of radiator and the amount of thermal energy Qp necessary for heating 1 cubic meter. meter of the room. The Q value must be indicated in the radiator's passport. The Qp value for the standard panel house room is 0.041 kW. For a brick house, this figure is reduced to 0.034 kW per 1 cubic meter. meter. For residential premises in which good thermal insulation, thermal power is even less - 0.02 kW.
The number of sections of the radiator is determined in the same way as the calculator of the heating battery by area, that is, by multiplying the volume of the room by the specific volumetric heat energy and then dividing by the value of the nominal heat flux of the radiator:
N = V x Qp / Qnom, pieces. The result is rounded up.
It is important! Since these calculations are rather approximate and do not take into account the thermal losses of the building, rounding to the large side will allow some reserve to improve the comfortable heating conditions.
Accounting for additional factors in thermal calculations of radiators
Additional factors affecting the heat transfer of radiators are correction factors that correct deviations from the standard conditions adopted in the basic calculations.
Height adjustment
The standard height of the room is 270 cm. In the case of a larger height, the correction factor is determined by dividing the height of the room by a standard value of 270 cm. That is, for a room height of 324 cm, the ratio will be 324/270 = 1.2. Accordingly, the specific heat output is 100 W per 1 sq. Km. meter should be increased by 1.2 times, that is, it will already be 120 watts per kV. meter.
The heat output of the heating batteries depends on the location, since the convection currents are mixed differently at different distances between the fins of the radiator and the floor or the window sill. Correction factors are shown in the diagram. At the same time, it should be borne in mind that for the corner rooms the heat loss is two times higher, since there are two windows in such rooms. 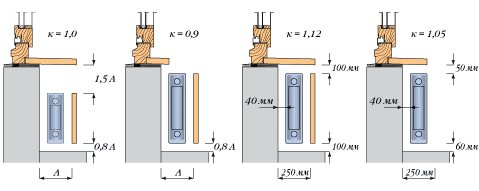
The coefficient of correction to the nominal value of heat dissipation of the radiator is the most optimal for diagonal connection of heating pipes. But the specific conditions for mounting the batteries do not always allow the use of this circuit. 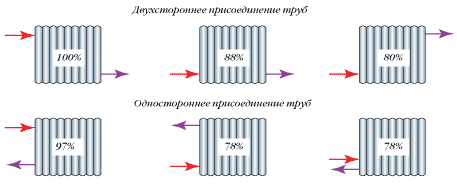
Summary
It is difficult to take into account all the factors influencing the heat transfer of the radiator. According to plumbers, if the house has the perfect thermal insulation, you can do without heating. There is enough heat from electrical appliances and a stove. It is also very important to be able to calculate heat loss, depending on the size of windows, doors and windows. However, the averaged values of the thermal characteristics of rooms and radiators are considered to be able to determine with a certain accuracy the required number of radiator sections and not to miss at room temperature.
The thermal calculation of the devices consists in determining the required nominal heat flux, the brand of the panel radiator or convector and the number of sections or columns of the sectional and tubular radiators. The calculation of heating devices is carried out according to the recommendations of OOO VITATERM. The technical characteristics of the heating system are adopted for the device with an interaxial distance of 500 mm (except for the convector).
The required nominal heat flux of the device, W, is determined by the formula
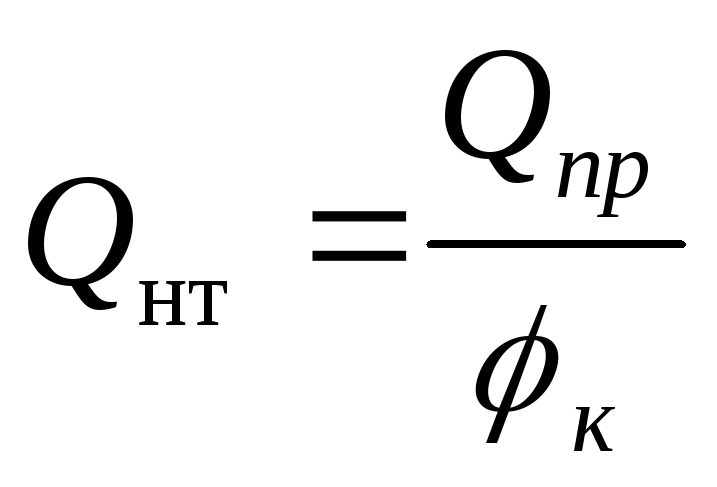 ,
(11)
,
(11)
where Q etc - required heat transfer of the device, W;
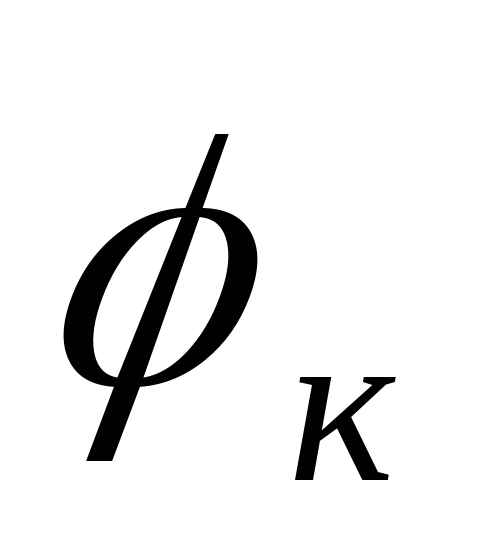 - complex coefficient of reduction to nominal conditions.
- complex coefficient of reduction to nominal conditions.
Heat output of the device Q etc , W, is calculated by the formula
Q etc = Q p – Q tr , (12)
where Q p - heat losses of the room, determined in the calculation of the heat balance (from Table 3) W;
Q tr - total heat transfer of pipes laid inside the room, W.
In the course work, the useful heat transfer of pipes Q tr , W, is taken in fractions of the heat losses of the room: in a two-pipe vertical heating system for the upper floor, the heat transfer of the pipes is 5% of the heat losses of the room and 15% for the remaining floors; 5% of the heat losses of the room.
The complex coefficient of reduction to nominal conditions is determined by the formula
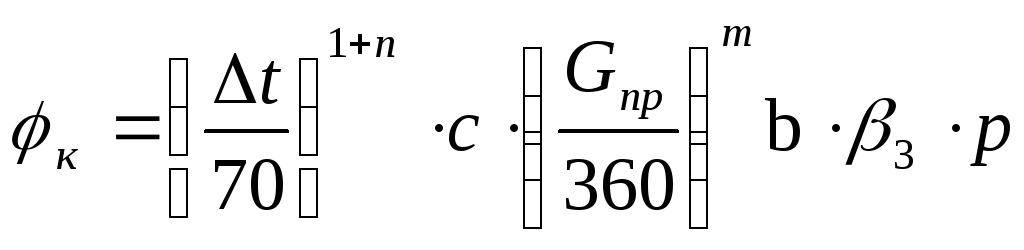 ,
(13)
,
(13)
where n, m, c - the empirical numerical values that take into account the influence of the flow pattern of the coolant on the heat flow and the coefficient of heat transfer of the device are given in the recommendations of OOO "VITATERM" under the most optimal scheme of water movement "from top to bottom";
p - coefficient takes into account the directions of coolant movement in the device;
b - The coefficient of atmospheric pressure in the area;
Δ t - the difference between the average water temperature in the device and the ambient air temperature in the room;
G etc - water flow through the device, kg / h.
The temperature difference in the device is determined by the formula
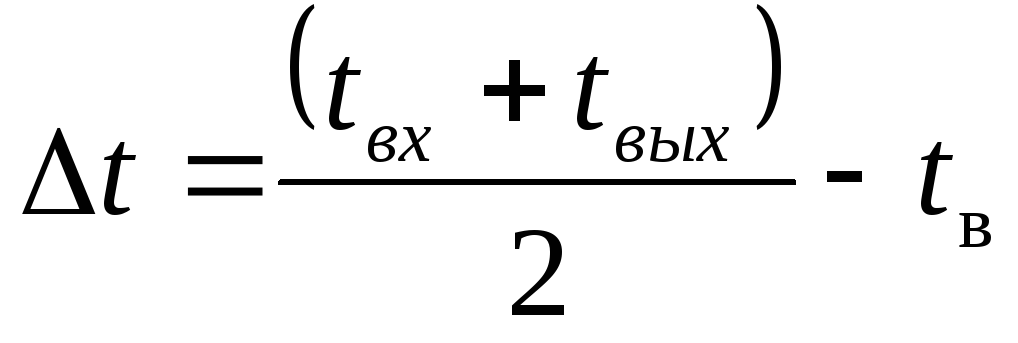 ,
(14)
,
(14)
where t in , t out - the temperature of the water entering and leaving the device, ºС, for a two-pipe water heating system with steel pipes should be taken t in = 95 ° C, t out = 70 ° C; with the distribution of polymer pipes, the temperature is selected depending on the characteristics of their material. For metal-polymer pipes t вх = 90 ºС and t out = 70 ºС; for polypropylene t in = 85 ºС and t out = 65 ºС.
Water flow through the heater 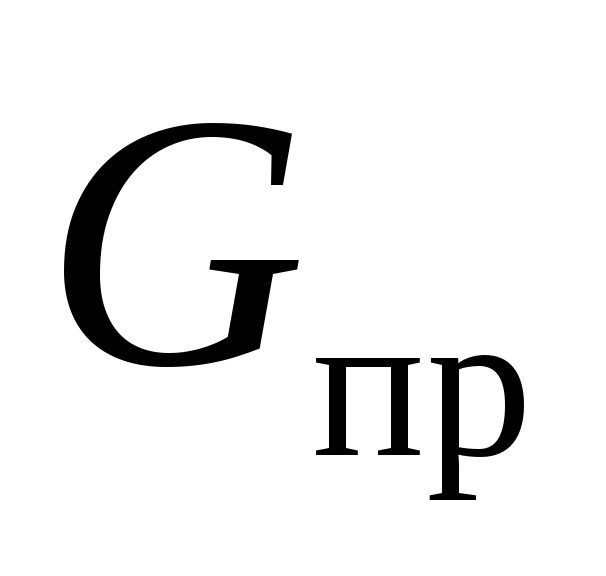 , kg / h, is determined by the formula
, kg / h, is determined by the formula
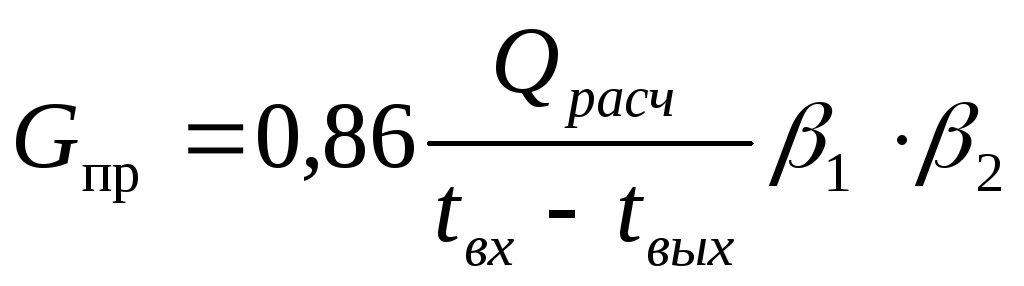 ,
(15)
,
(15)
where 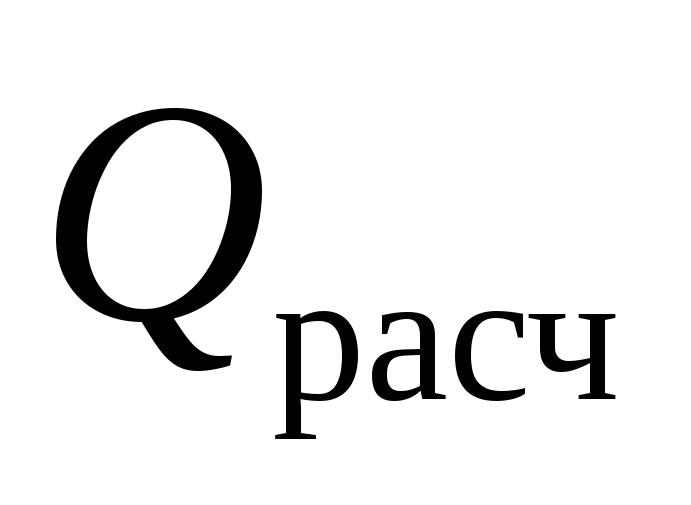 - heat loss of the room from Table 3, W;
- heat loss of the room from Table 3, W;
β 1 - coefficient depending on the step of the nomenclature of the device;
β 2 - coefficient depending on the type of device and method of installation.
Both coefficients are selected according to the table.
The number of sections of the heater is determined by the formula


 ,
(16)
,
(16)
where 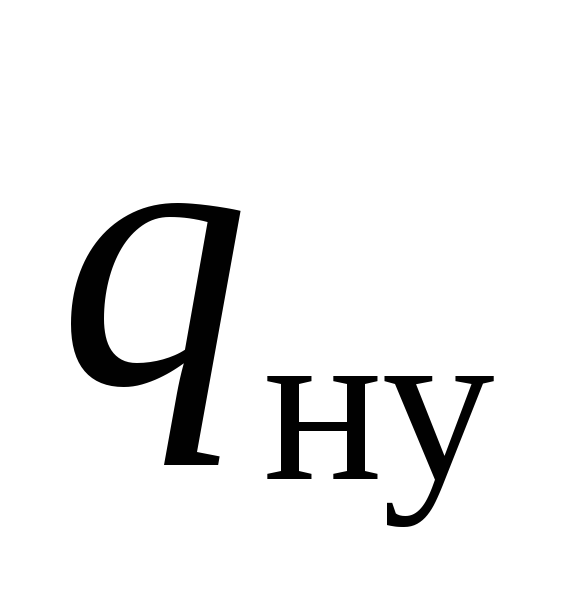 - the nominal heat flow of one section, W, is given in the recommendation for calculating the heater, table;
- the nominal heat flow of one section, W, is given in the recommendation for calculating the heater, table;
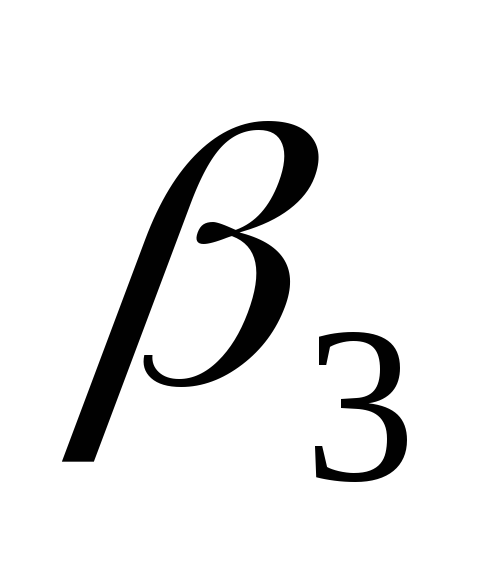 - coefficient characterizing the dependence of heat transfer of the radiator on the number of sections, table.
- coefficient characterizing the dependence of heat transfer of the radiator on the number of sections, table.
Thermal calculation of heaters should be performed in tabular form.
Table 4 - Thermal calculation of heating devices
|
No. of riser, room no. |
Heat loss of the room Qrec, W |
Heat transfer of pipes Q tp, W |
Required heat dissipation of the device Qpr, W |
Coefficient β 1 |
Coefficient β 2 |
Air temperature in the room t in, 0 С |
The temperature of the water at the entrance to the device t in, 0 C |
The temperature of the water at the outlet of the device t out, 0 С |
Temperature head Δt, 0 С |
Water flow through the device G pr, kg / h |



