Heating system with forced circulation circuit. Heating system with forced circulation: advantages, disadvantages, types. Principles of calculation and compensation of the system
The effectiveness of the system with forced circulation The heat carrier is achieved due to the ability to control and set the desired level of heating in each room and for each radiator. From the point of view of the owner, this nuance sometimes acts as a decisive factor in choosing the type of system.
Turning to other benefits heating system with forced circulation for a single-storey house, it is worth noting:

Analyzing the drawbacks of the scheme with forced circulation, it is worth mentioning the main ones. First of all, in the absence of electricity, there will be no heating in the house. It is not recommended to use such a system if the area is characterized by interruptions with electricity. Experts note another drawback - the creation of noise during the operation of the circulation pump. But it can be solved. For example, installing a boiler and pump in a non-residential room, boiler room, basement.
Choosing modern versions of boilers, it is worthwhile to know that almost all of them are equipped with a built-in pump. He works, of course, not noiselessly, but not so loud as to be considered a problem. For example, the hood in the kitchen makes a lot more noise.
The main components of the system
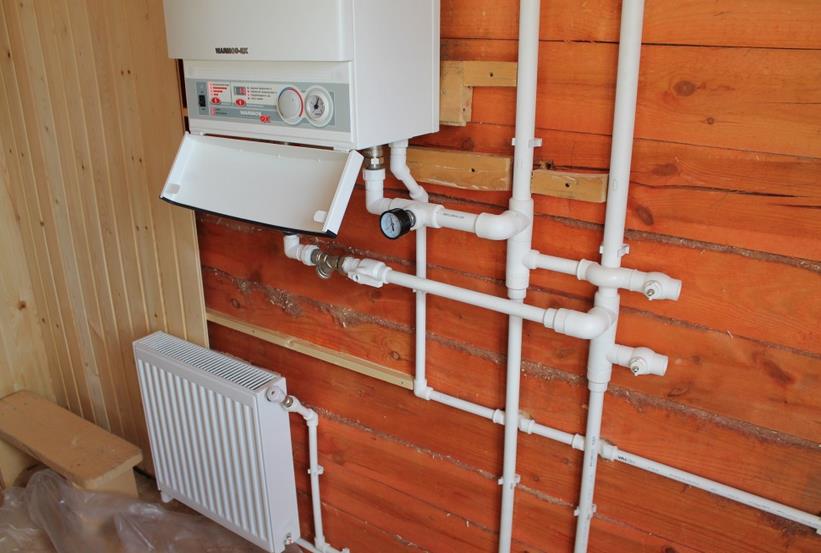

On the type of the boiler depends the need to install the pump and expansion tank. All modern models are equipped with them (except for solid fuel).
To draw a diagram of heating a single-storey house, you need to determine its main components. First, pick up the boiler. Type the boiler based on the availability of resources (gas, solid fuel, combined, electric). If possible, it is worth giving preference to the equipment with closed camera combustion (except solid fuel) and a turbocharged chimney. This is the safest and less labor intensive in maintenance and operating conditions. If you need to ensure the heating of water for housekeeping needs, it is worth taking a two-circuit.
The calculation of power takes place taking into account all possible heat losses. But the minimum parameter can be calculated by the area: 10 kW for a house in 100 sq.m. Usually take with a margin for hidden heat loss (better to add from 20%). Add 50% of the initial value to the DHW circuit.

When calculating the power, one must take into account the heat loss
If the boiler has an expansion tank and a pump, they do not need to be installed separately. Otherwise, the pump is selected according to the following parameters:

Today there are two main types, which differ in the way of installation and the device, the so-called dry and wet type pumps. In terms of work efficiency, they do not have any significant differences.
For a small single-storey house (up to 200 sq. M.) There will be enough equipment with a capacity of up to 3.5 m3 / h and up to 0.4 atm pressure. Installation of the pump is recommended to carry out reverse flows on the pipe, since it contains already cooled coolant. This will extend its service life.
Often, sellers or specialists note that modern pumps contain ceramic seals that can withstand up to 110 ° C, but take precautions will not be superfluous.
Types
When designing a scheme for a single-storey house, it is worth considering the features of the versions of the systems with forced circulation.
If you choose a single-pipe system, you should consider the possibility of disconnecting each battery (for repairs, adjusting the temperature in the room)
This is relatively rarely used because of low efficiency. It represents one highway along the walls, passing under all the radiators. From each of them, nozzles are installed in it, through which the supply and removal of the coolant takes place. As the hotter coolant enters the first radiators, giving them some of the heat, the latter approaches the last cooled down already. As a result, heating the house will be uneven, and the farthest from the boiler rooms will heat up much longer. Best of all, this scheme is suitable for a single-story house in a small area, as it will reduce the cost of installation. There is another version of the single-tube scheme: when the radiator cuts into the pipe. The downside of this method is the impossibility of covering one of the radiators so that the entire system can not be stopped.
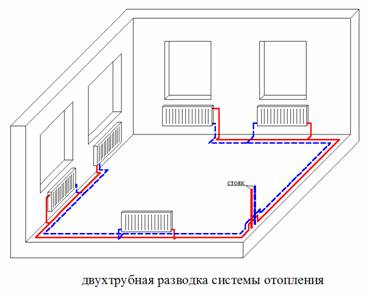
Choosing a two-pipe system, you can connect the radiators by any means: diagonal, lateral, lower connection
Scheme of a two-pipe system for heating a single-storey house
This is the optimal heating scheme, which is suitable for a single-storey house of a large area, as well as for a two-storey building. Its meaning lies in the separation of coolant flows: a separate pipe for supply hot water to radiators and the second - for the removal of cooled down. From the shortcomings of the scheme, you can identify a large consumption of material, since it will be necessary to mount two separate lines along the entire perimeter of the house. But the advantages of the system are more significant: the difference in the temperature of the coolant, which is suitable for the first and last radiator, is not significant. Depends on the size of the house and the number of batteries.
The most effective system, but also the most costly, requiring compliance with certain conditions and a professional approach when starting up
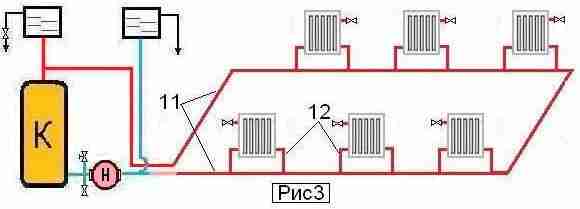
Collector (beam). This scheme will ensure the supply of the most hot coolant to each battery. For a single-storey house is chosen rarely, only with a large area, but collector system is most appropriate for two-story house. It represents the supply of the coolant through one pipe, from which the branch branches into each room and diverges by the radiators. It is allowed in some cases to apply a scheme for only one room, for example, with a large number of batteries. But this system often involves laying in the floor, which is not always possible, and costly due to a large consumption of material.
Radial and two-tube systems can be combined, it is also possible to draw in the scheme the use of a warm floor system in one or more rooms.
- serial and parallel. Serial connection is achieved by means of single-pipe wiring, parallel - using a two-pipe heating system.
One- and two-pipe heating systems
With a parallel wiring (two-pipe private house), each battery receives a heated coolant from the supply pipe and returns to the "return". Pipes for installation need twice as much, but there is an opportunity on each battery, reducing the temperature in uninhabited rooms and thereby saving fuel.
A special case of such a connection is the beam scheme, we will not consider it here due to the complexity of the adjustment and the high consumption of materials.
Scheme of 1- and 2-pipe heating system
In a sequential wiring (single-pipe heating system), the coolant from passes consistently all, giving away each part of the energy.
This is the most simple circuit, requiring the least amount of materials. Bad in it is that the radiator nearest to the boiler will be the hottest, the farthest, the coldest.
In addition, it is not possible to regulate the heat dissipation of individual radiators. This scheme is almost not used today.
Heating systems with natural and forced circulation
The most widely used in our country - water heating. In the pipe, the coolant can move either naturally or forcedly by the pump.
In the heating system with natural circulation, the heat carrier, expanding from the heating in the boiler, creates pressure in the heating system and moves along the contour, gradually cooling in the radiators.
Such heating does not require electricity for operation, it is simple in the device, but the correct selection of the pipe diameter is important, and the angles of the pipe gradient are accurately observed at.
The heating system with natural circulation is used for low-power boilers and small rooms (apartments, small country houses for 2-3 rooms). The total length of the circuit should not exceed 30 m. The efficiency of this principle of heating the house is lower than that of the forced circulation circuit.
The heating system with forced circulation of the heating medium has a built-in circulation pump, which is always mounted in the pipe "reverse". This eliminates the contact with the hot coolant and increases the pump service life. The pump can be used one or more, depending on the size of the house, the number and length of the wiring contours.
Characteristics of forced circulation
- independence of coolant temperature
- extension of contours
- design decisions in the design of heating
- possibility of operating mode control
- dependence on electricity
The pipes leading to the boiler can be non-metallic. It can be, metal-plastic, it is important that they have a maximum operating temperature of 95 ° C.
Open and closed heating circuits
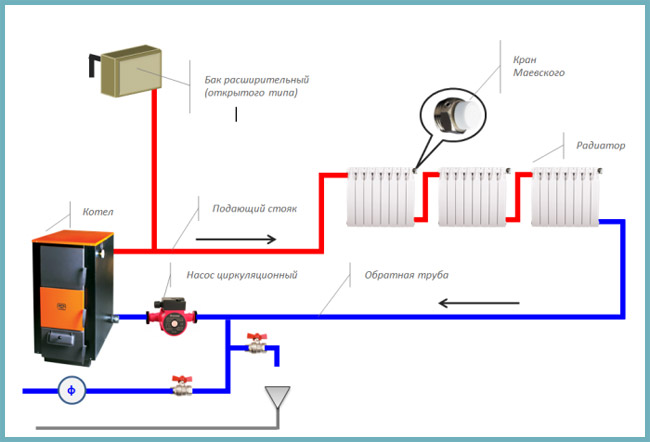
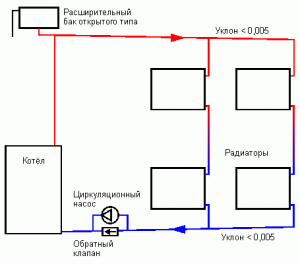
Open called heating wiring, in which the coolant (usually water) communicates with the atmosphere. They have, in which, if necessary, water is added. Changes in the volume of the heating medium caused by heating in the boiler lead to an increase or decrease in the water level in the expansion tank. An open system requires periodic monitoring of the coolant level. Has missed - water can boil in the boiler and disable the equipment.
More common and economical is a closed two-pipe heating system with forced circulation. For its correct functioning, additional devices must be installed.
In contrast to open, closed systems do not have contact with the atmosphere. To control the increase and decrease of the volume of the heat carrier, a membrane expansion tank. It is a sealed container, internally divided into two parts by a flexible membrane. One of the parts is filled with air or nitrogen under pressure. The second one is connected to the heating circuit pipes. This design successfully compensates for the sudden increase or decrease in pressure in the pipes, preventing breakdowns due to sudden overloads. The size of the tank is selected in a volume comparable to the thermal expansion of the coolant in the system. Approximately 10% of the total amount of coolant. It is necessary to control the pressure in the heating system in accordance with the design requirements of the boiler and pump.
Diaphragm tank for heating - installation
The expansion vessel must be pumped up to the design pressure before installation or checked. manufacturers, as a rule, supply already inflated membrane tanks. AT household systems The pressure fluctuates around 2-2.5 bar, but does not exceed 4 bar. Where to install the tank? To the pump on the return, closer to the boiler. In the case of an emergency increase in pressure in the pipes, more than the membrane expansion tank can withstand, safety valve.
Automatic air vent
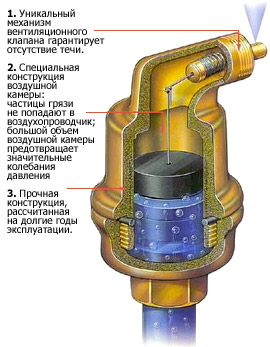
It is very simple. Simpler, the device can be described as a flask with a float. When air accumulates in the flask, the float descends and opens the valve for air. The heat medium under pressure fills the flask, raising the float and locking the valve. The most practical models - with a shut-off valve, which makes it possible to freely screw - unscrew the air vent without spilling the coolant. Because of poor-quality coolant, the air separator can fail more often than other elements of the boiler house. All faults of this node are manifested as a leak and are caused by two reasons:
- The needle is clogged with hardness salts. It is eliminated by the cleaning of the needle and the rocker mechanism. It is enough to unscrew the lid, after the stripping, collect everything.
- Breaking the integrity of the gasket (ring) under the housing cover. Change the gasket, or on the thread, which fastens the lid, make several turns of the tape.
Removal of air should be provided and in other places of the outline - on risers, combs and each heating device. Recently, on the radiators, instead of the usual valve of Majewski, angular automatic air separators began to be installed. This is important for heating circuits that have been installed long ago and incorrectly. In order not to suffer, regularly bleeding air from the pipes, it is better to put an automatic air vent. Important detail - When installing, make sure that the nipple is pointing upwards, otherwise the float will not work.
All modern technologies and design solutions are aimed at reducing operating costs for space heating - reducing fuel consumption, reducing the cost of maintenance. But the most unpleasant thing is that, no matter how much fuel consumption is reduced, no matter how cheap a fuel is found, we have to pay for it, and the burned fuel will give us less than half the heat received according to the laws of thermodynamics. It is sad.
There is a solution when you do not need to pay for fuel and the cost of maintenance equipment will be a mere trifle. This is geothermal.
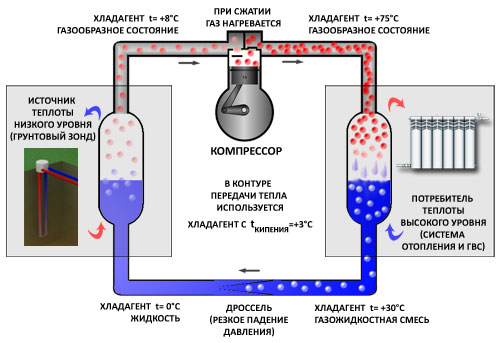
Heat pump - the principle of operation
Any refrigerator, taking heat from a closed volume, gives it to the environment. The heat pump, on the contrary, takes heat from the environment, cooling it, and pumps it into the closed volume of the house. This is the case: a well was drilled in the area near the house, or a trench was dug below 1 m, where the pipes were laid. At this depth, the temperature is practically constant and is about 10 ° C. The water is pumped through the pumps and gets the same temperature as the earth. In the house, in a special heat exchanger tank, water transfers the temperature of the earth to freon. Then freon is compressed by the compressor and from compression is heated up to 60 0 C. In the other device - the condenser - it gives these 60 0 С to the heating system of the house. Then the cold gas is again heated to 10 0 C and the cycle is repeated.
This is a very primitive description, but the point is that energy (electric) is spent only on pumping water through underground pipelines, compressor operation and forced coolant circulation. 1 kW of electricity consumed brings about 3.5-4.5 kilowatts of land heat to the house. Therefore, it is said that the efficiency of the heat pump is higher than 100%. Heating systems based on a heat pump have a lot of good properties:
- They are noiseless as a refrigerator
- Fireproof
- Have a long service life (up to 50 years of well, up to 20 years of equipment)
- Easily Automated
- One and the same equipment heats in winter, air-conditioning in the summer
- No harmful emissions
Boiler
So, the payback period of the heat pump in comparison with other options for obtaining heat is 3-7 years, and taking into account the constant increase in energy prices, there may be even less. If we receive electricity from renewable sources, complete autonomy of heating and zero operating costs will be ensured.
Considering the arrangement of the heating system for a single-storey house, the owner has to choose between two absolutely opposite options: heating with natural and forced circulation. In the first case, the rate is made for basic physical laws, and in the second case for special equipment. And for a variety of reasons, the second option is often found in the favorites. Why is it so remarkable? To find the answer, we offer to understand the principles of operation and specificity of the system with forced circulation, as well as get acquainted with the rules and video of the organization of different heating schemes with their own hands.
Principal differences
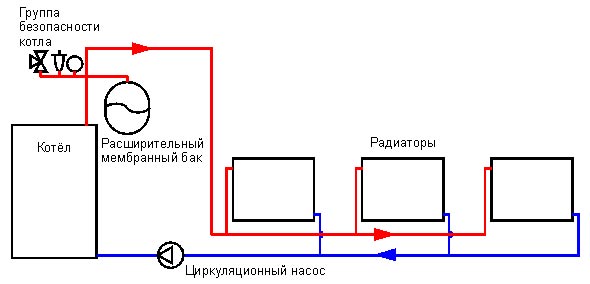
The main feature of the considered is the presence of a pump. He receives and sends it further according to the scheme to the heating devices. Here, the physical principle of the natural motion of the liquid does not play a role because of the difference in the temperature indices - the coolant moves in the required direction forcibly with the given parameters of speed, temperature and pressure without loss of heat. The standard heating system includes the following components:
- boiler;
- pump;
- expansion tank;
- radiators;
- pipes;
Heating system with pump
- connecting fittings;
- air outlets;
- ball and cork cranes;
- filters;
Council. Choosing equipment for the operation of a heating system in a particular single-story house, three important factors must be considered: the capacity of the boiler used, the length of the pipeline, the planned rate of movement of the coolant.
There are two schemes of a heating system with forced circulation: one-pipe and two-pipe.
Single-pipe heating system
The main difference between a single-pipe heating system is the combination of two lines: supply and return. This makes it possible to use fewer pipes and accompanying equipment.
In a single-storey house, a horizontal or vertical version of a single-pipe heating system may be used. Both are suitable mainly for small houses.
The horizontal system works in this way: the coolant enters the main line and, distributed along the horizontal supply risers, evenly moves to all the radiators.
The vertical single-tube system is characterized by the fact that in it the coolant moves along the supply risers from the top to the bottom: first from the boiler it enters the main pipeline located in the attic or attic, and from it to the batteries of the ground floor.
Single-pipe system heating systems
In both cases, after cooling, the coolant returns to the heating boiler - it flows there along a combined return line through a pumping unit.
Two-pipe heating system
The two-pipe system is distinguished by a distinction between the supply and return main pipelines. It is represented by two types: horizontal and vertical schemes. Additionally, both these schemes are divided into several more types.
The horizontal scheme is performed in three variations:
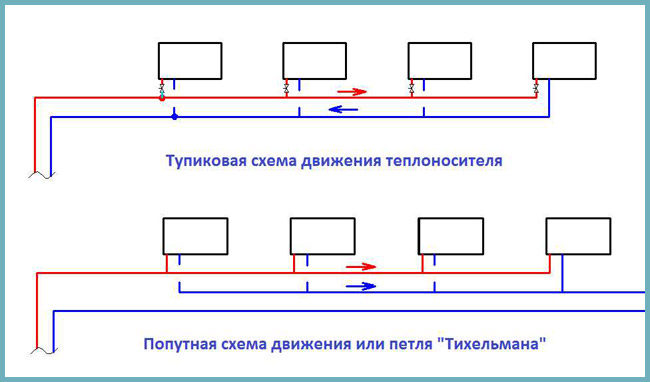
- Dead-end - means that each subsequent battery in the course of moving the coolant is located farther from the boiler, which increases the circulation circuit and reduces the efficiency of control over the heating system.
- Passing - has equal circulation contours, which increases the length of the pipeline, but allows you to facilitate and improve control over heating.
- Collector - involves a separate connection of each radiator, which ensures a uniform heating, but requires the use of a large number of pipes.
The vertical scheme is performed in two variations:
- With the lower decoupling: first the coolant is fed through the pump into the supply pipes, through them to the batteries, and after the heat is released - back to the boiler along the return line of the pipeline.
- With the upper denouement: the coolant is fed to the main pipeline, located in the attic, attic or under the ceiling, then from there goes through the supply pipes to the batteries, and then goes to the return line of the pipeline laid in the basement and returns to the heating boiler.
Two-pipe heating system
Advantages and disadvantages
Due to the use of the pump, the heating system with forced circulation type has a considerable range of advantages:
- The possibility of using pipes of any diameter - the quality of the system's operation is not tied to the diameter of the pipes, since the pump guarantees a constant velocity of the coolant moving and the same heating of all zones of the system, regardless of the size of the used products. This allows to ensure the smooth operation of the system even with inexpensive pipes of reduced diameter.
- Simplified installation - there is no need to strictly maintain a certain angle of laying pipes, as in the case of a system with a natural type of circulation, which makes it possible to perform the installation of equipment yourself.
- Independent temperature control - it is possible to set a specific temperature in each separate room of a single-storey house, regardless of the temperature in the neighboring room.
- Absence of temperature differences - thanks to the pump in the system there are no significant temperature fluctuations, which significantly increases the service life of all devices and units.
Piping heating pipes in a private house
Among the main disadvantages:
- Dependence of heating on electricity supply - due to the use of a circulating pump, the heating system requires a mandatory connection to the mains.
Council. The pump can be protected from emergency power outages by using an uninterruptible power supply.
- Uncomfortable noise level - work pumping unit is accompanied by not very pleasant noise.
Without a doubt, the heating system with forced circulation in many respects exceeds the option with a natural movement of the coolant. That's why it is most often chosen for single-storey houses. But for this choice to bring only positive results, it is important to organize heating correctly, so carefully study the available schemes of the device system - they are all in front of you.
Diagram of a single-pipe heating system: video
Heating system for a private house: photo
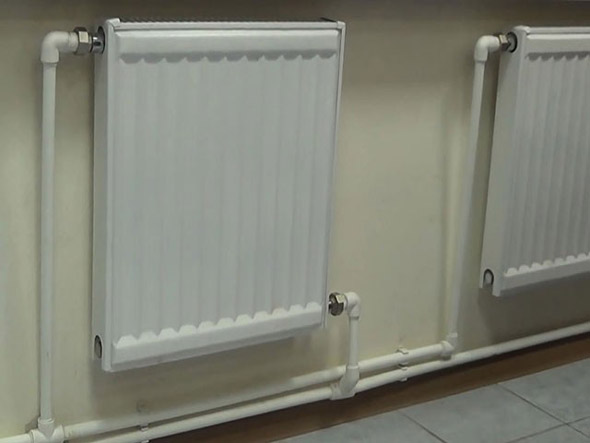
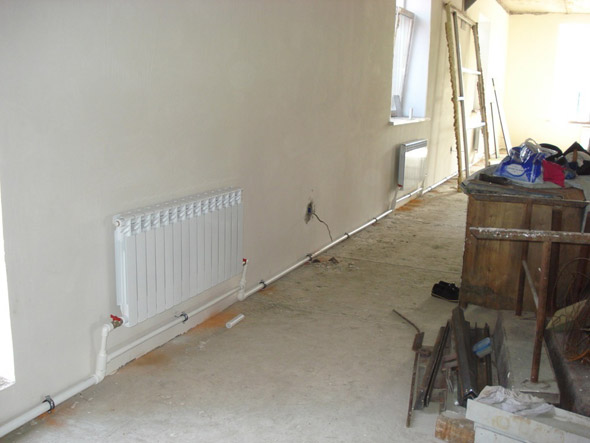


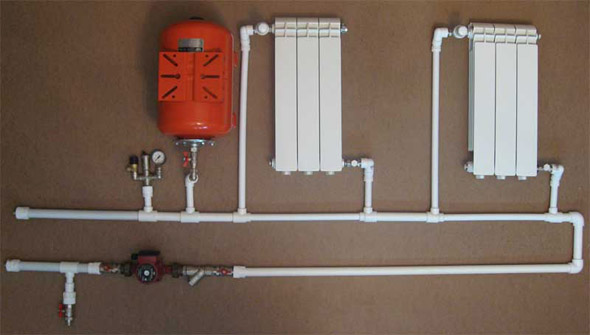


Unfortunately, the history did not retain the name of the inventor of water heating, it is known only that it appeared long ago. And all this time the schemes of water heating occupied a leading position. Years passed, created economical boilers for different types of fuel, new heating schemes were developed, radiators were manufactured on the basis of the latest materials. But there is still no alternative to a water heating system. It is easy to install, the elements of the system are easy to purchase, and its operation does not cause problems. A popular heating scheme with forced circulation is very effective for creating comfort in the house.
Classification by the method of moving the coolant:

Simple schemes of gravity heating can only be open, circuits with forced circulation are usually closed with a sealed membrane tank. If you install the pump in the "return" of the gravity flow system, the efficiency of the circuit will increase.
 Today you can buy a boiler of any capacity, working on various fuels. There are boilers of world famous brands, pipes made of metal and plastic, armature. There is all necessary for installation of heating circuits of any configuration and power. Today, any heating system of a private house with forced circulation is designed and created without problems, with the availability of certain financial resources.
Today you can buy a boiler of any capacity, working on various fuels. There are boilers of world famous brands, pipes made of metal and plastic, armature. There is all necessary for installation of heating circuits of any configuration and power. Today, any heating system of a private house with forced circulation is designed and created without problems, with the availability of certain financial resources.
Basic requirements for heating systems:
Which is better, forced or natural movement of water
 In the contours conditions are created for the movement of the coolant under the influence of gravity and the slope of the pipelines, an open expansion tank is installed. This creates a self-heating system for heating a private house, cheap, simple and reliable. The pressure line rises upwards to create pressure in the system. When installing pipelines, both the pressure head and the return pipe, a slight slope is maintained in the direction of the water flow. The velocity of the coolant is insignificant, therefore, to increase the efficiency, larger diameter pipes are installed.
In the contours conditions are created for the movement of the coolant under the influence of gravity and the slope of the pipelines, an open expansion tank is installed. This creates a self-heating system for heating a private house, cheap, simple and reliable. The pressure line rises upwards to create pressure in the system. When installing pipelines, both the pressure head and the return pipe, a slight slope is maintained in the direction of the water flow. The velocity of the coolant is insignificant, therefore, to increase the efficiency, larger diameter pipes are installed.
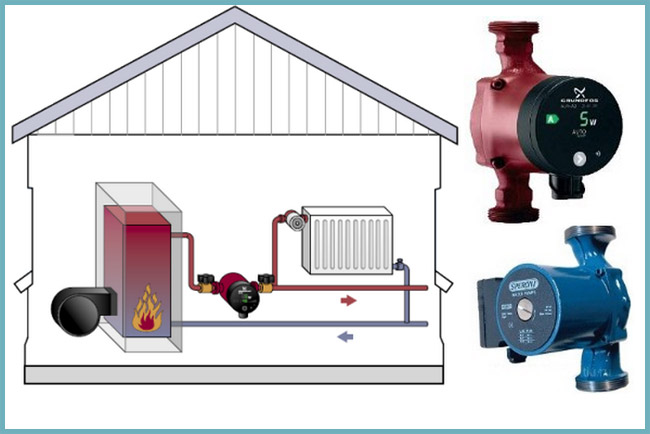
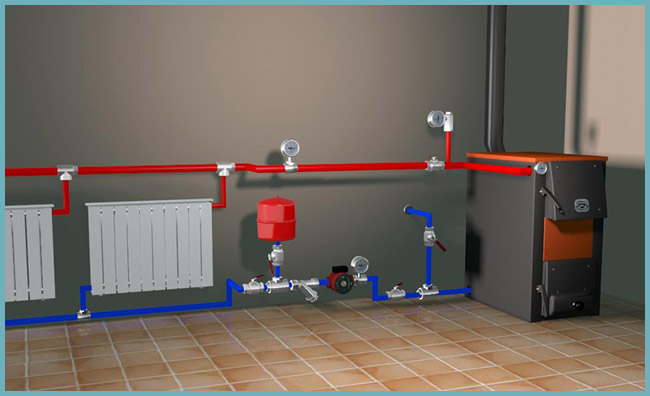
The system of water heating with forced circulation, which is used more often, is mounted with. It is integrated in the boiler or installed separately. The presence of the pump increases the efficiency of the system and saves fuel.
Advantages of systems with a circulation pump:
The disadvantage, which has a scheme of heating the house with forced circulation - dependence on electrical network. If there are problems with power supply in the region, then special devices can be used to organize uninterrupted power supply from the battery. For boilers use UPS (), for example, the company SinPro. It automatically switches on and provides power to the circulation pump. The second drawback is the noise generated by the operating circulating pump. When installing the boiler in a non-residential room, this disadvantage can be neglected.
One and two-pipe heating systems
Many heating schemes have been designed and installed. But all of them are modifications or combinations of two variants of systems that can be defined by basic variants.
Basic or basic schemes can be considered: 
- single-tube;
- two-tube.
Single-pipe heating circuit
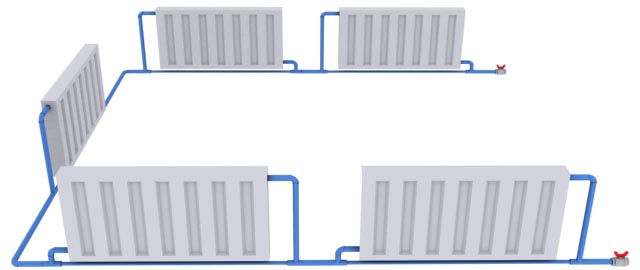 Is simple simple, how does it work? Simple, extremely simple. From the boiler, one hot tube passes a hot coolant and, passing a successive chain of batteries, returns to the boiler. This principle really uses the scheme of heating a single-storey house with forced circulation, and installing a bypass on the pump turns it into a "gravity" system.
Is simple simple, how does it work? Simple, extremely simple. From the boiler, one hot tube passes a hot coolant and, passing a successive chain of batteries, returns to the boiler. This principle really uses the scheme of heating a single-storey house with forced circulation, and installing a bypass on the pump turns it into a "gravity" system.
Disadvantages of a single-pipe system: 
- uneven heating radiators;
- to replace the battery, you must disconnect the system.
 The drawbacks of the above scheme are practically eliminated in the modernized single-pipe circuit heating, which is known as the "Leningrad", at the place of its invention in St. Petersburg. In St. Petersburg "Leningrad" is used even in multi-storey buildings. Ball Valves at the input / output of the battery will allow you to replace or repair the batteries without turning off the heating. Batteries cut into the feed pipe in parallel.
The drawbacks of the above scheme are practically eliminated in the modernized single-pipe circuit heating, which is known as the "Leningrad", at the place of its invention in St. Petersburg. In St. Petersburg "Leningrad" is used even in multi-storey buildings. Ball Valves at the input / output of the battery will allow you to replace or repair the batteries without turning off the heating. Batteries cut into the feed pipe in parallel.
When organizing the heating scheme of a two-story house with forced circulation, a vertical wiring diagram is mounted.
 The pipeline rises to the second floor, water enters the batteries horizontally arranged in series. Then, from the last radiator, the pipeline goes down and connects to the horizontal ruler of the radiators, and then the coolant that gives up its energy flows into the boiler. A disadvantage of this system is the uneven heating of the radiators. This drawback is especially noticeable if "self-tracking" is used, but if the circulation pump is installed, the temperature difference is almost invisible.
The pipeline rises to the second floor, water enters the batteries horizontally arranged in series. Then, from the last radiator, the pipeline goes down and connects to the horizontal ruler of the radiators, and then the coolant that gives up its energy flows into the boiler. A disadvantage of this system is the uneven heating of the radiators. This drawback is especially noticeable if "self-tracking" is used, but if the circulation pump is installed, the temperature difference is almost invisible.
Two-pipe heating circuit
 The most optimal are the schemes of heating systems with forced circulation in the circuit. Such systems are effective for single-storey cottages, houses and villas and will easily provide heat two-storey house large area. For the implementation of this scheme, two pipes are installed: a supply pipe and a return pipe. Batteries are connected in parallel, they are supplied with shut-off valves and devices for air removal. This scheme ensures uniform heating of the batteries, but the pipe consumption for installation is much larger. Additional costs are compensated by efficient heating operation.
The most optimal are the schemes of heating systems with forced circulation in the circuit. Such systems are effective for single-storey cottages, houses and villas and will easily provide heat two-storey house large area. For the implementation of this scheme, two pipes are installed: a supply pipe and a return pipe. Batteries are connected in parallel, they are supplied with shut-off valves and devices for air removal. This scheme ensures uniform heating of the batteries, but the pipe consumption for installation is much larger. Additional costs are compensated by efficient heating operation.
Vertical two-pipe circuit
 Vertical closed heating system with forced circulation scheme is implemented in two versions - with the lower (horizontal) or top wiring. Horizontal layout is organized as follows. The "feeder" pipe rises to the upper floor, all the batteries connected to the "return" are connected to it. Disadvantage - the presence of two pipes in the room.
Vertical closed heating system with forced circulation scheme is implemented in two versions - with the lower (horizontal) or top wiring. Horizontal layout is organized as follows. The "feeder" pipe rises to the upper floor, all the batteries connected to the "return" are connected to it. Disadvantage - the presence of two pipes in the room.
Vertical two-pipe system second option
 Vertical two-pipe wiring significantly less affects the interior, because through the room there is one pipe and it's easier to hide. The delivery rack rises to the attic, then the pipe goes down and feeds the radiator. The radiator on the second floor is connected in series with the radiator of the lower floor and already from it the water enters the pipeline "return" on the lower floor. So it functions closed system heating with forced circulation, made on a vertical two-pipe scheme.
Vertical two-pipe wiring significantly less affects the interior, because through the room there is one pipe and it's easier to hide. The delivery rack rises to the attic, then the pipe goes down and feeds the radiator. The radiator on the second floor is connected in series with the radiator of the lower floor and already from it the water enters the pipeline "return" on the lower floor. So it functions closed system heating with forced circulation, made on a vertical two-pipe scheme.
Branch wiring diagram
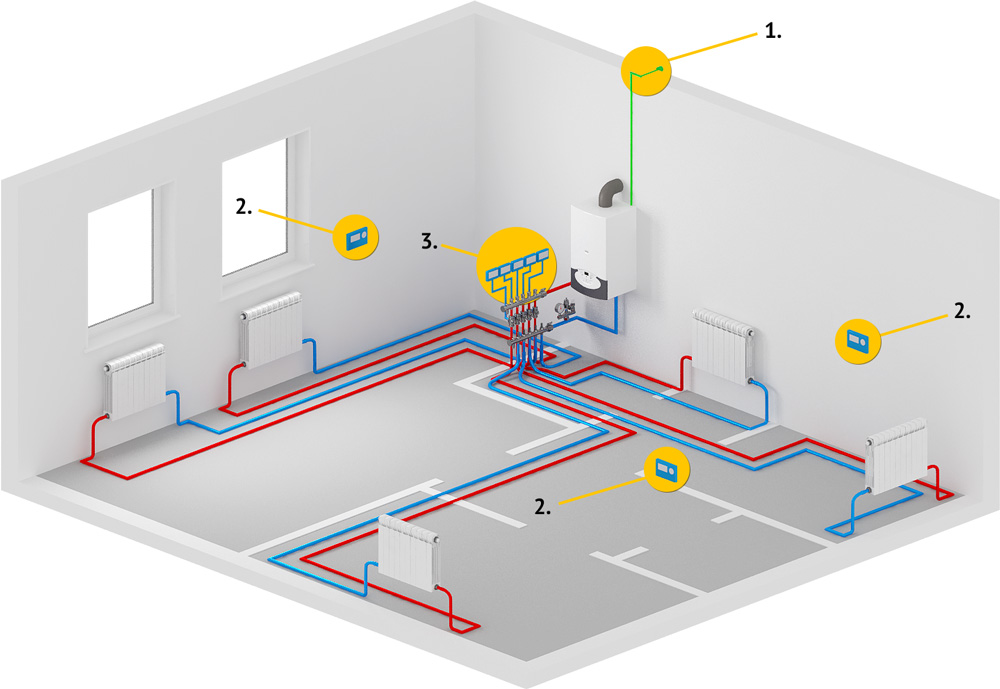
For complex contours, with a large number of connections, it is mandatory to organize forced circulation in the heating system with the distribution of the coolant through the collector.
This distribution system has found application for two-story houses or single-storey houses with a large heating area.
 Sometimes combined wiring is used, and for a complex configuration of the system an additional pump for the heating system with forced circulation is optimized to optimize the functioning of the system.
Sometimes combined wiring is used, and for a complex configuration of the system an additional pump for the heating system with forced circulation is optimized to optimize the functioning of the system.
 If the house already has a heating circuit that uses natural circulation, then the efficiency of such a heating system can be improved by installing it in a "return" near the boiler. As a result, a open system heating with forced circulation, the circuit does not require any changes.
If the house already has a heating circuit that uses natural circulation, then the efficiency of such a heating system can be improved by installing it in a "return" near the boiler. As a result, a open system heating with forced circulation, the circuit does not require any changes.
Generalization
A realized heating system with forced circulation scheme which can be any, will provide better heating of the home. The cost of creating such a system is greater than the installation of a system with natural circulation, which will pay off due to more economical fuel consumption.
Possible options for organizing heating systems (CO) are only two: 
- system with forced movement (PC);
- system with natural circulation of liquid (EC).
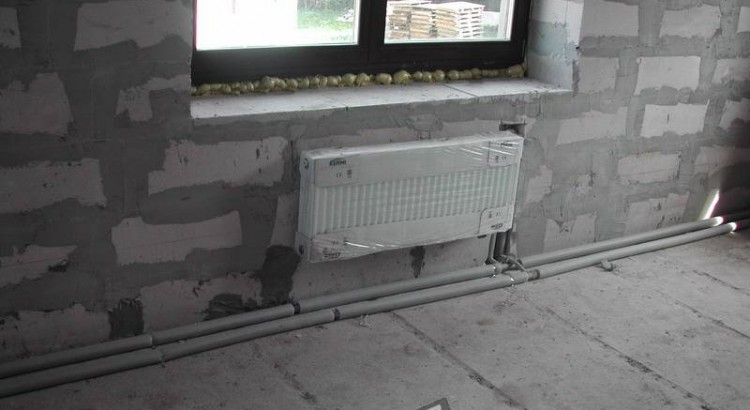 The system (EC) has an open expansion tank, and when installed in the "return" of the circulating pump it works quite well. The pump increases the efficiency of the system. The PC system refers to closed systems, and expansion of the heat carrier is compensated in a closed membrane tank. These are basic systems, and the basic schemes are one-pipe and two-pipe. Based on these basic elements, heating circuits are created that are a combination or upgrade of the basic systems and basic schemes.
The system (EC) has an open expansion tank, and when installed in the "return" of the circulating pump it works quite well. The pump increases the efficiency of the system. The PC system refers to closed systems, and expansion of the heat carrier is compensated in a closed membrane tank. These are basic systems, and the basic schemes are one-pipe and two-pipe. Based on these basic elements, heating circuits are created that are a combination or upgrade of the basic systems and basic schemes.
What is included in this system?
Circulation pump
How to choose a pump?
How do I install the pump?
Expansion tank
Installing the expansion tank
Security group
Mounting Features
Man has always tried to arrange his home so that it was warm. After all, it depends not only on comfort, but also on health. Today, there are different options available for heating the house. However, as time has shown, it is best to use water heating. But it must also be properly designed and arranged. If you make a mistake, it will lead to inefficient operation of the system, and uneconomical energy consumption. The most the best option, is heating with forced circulation. What are its advantages? Than it differs from natural circulation? What elements are included in such a system? These issues should be given due attention.
What is forced circulation and what are its benefits?
The principle of heating with forced circulation is easy to understand. If in a conventional system the coolant moves through the pipes due to physical laws (it expands when heated), here, it moves due to the action of the pump. It is this apparatus that increases the velocity of the liquid in the main line. Since the circulation does not pass by itself, it is called forced circulation.The advantages of this kind of heating
Of course, if you compare both types of circulation, then compulsory will require large material costs. But is it worth it? To answer this question, it is necessary to look at the advantages of forced circulation over the natural one.forced circulation circuit
- Since the coolant moves slowly along the main line during natural circulation, while it reaches the last radiator, it already distributes most of the heat. But in forced circulation, due to the high speed, the liquid transmits to all batteries a uniform heat, which guarantees the same heating of all rooms.
- This type of heating will warm up the cold room much more quickly.
- Eliminates the constant problem of heating systems - zvozdushennost. The pump will not allow air to form in the main.
- It is more possible to regulate the temperature separately in each room.
- Due to the fact that the pump is used, it is possible to put a closed or membrane expansion tank. This eliminates the need for constant monitoring of the water level in this tank.
- As calculations and experience show, such arrangement of the system saves fuel for heating. In turn, this minimizes the financial costs of heating.
- Much simpler calculation and installation of the system. With natural circulation, it is necessary to observe the correct slope, diameter, length of pipes, otherwise it will not work. With a forced system, all this is unnecessary, since the pump pushes the coolant in all conditions.
- Increases the service life of all heating elements.
- You can save on buying pipes of smaller diameter.
What is included in this system?
Here is a list of what is needed to equip the heating system with forced circulation:- boiler,
- circulation pump,
- expansion tank,
- radiators,
- filters,
- pipes,
- valves and air vent,
- ball and cork cranes,
- various fasteners.
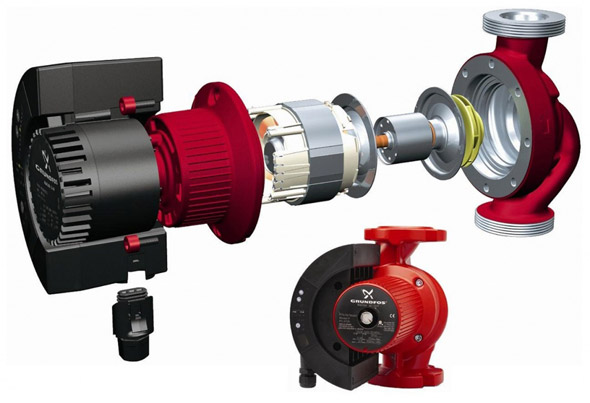
Circulation pump
Perhaps, this is the most important equipment for forced system. The pump imparts velocity to the heat carrier. On the one hand, it sucks in the liquid, but on the other it pushes it out. This device prevents the appearance of air plugs in the main, and also helps to evenly distribute the temperature across all radiators. The larger the heated room, the more necessary the circulation pump. circulating pump for heating
circulating pump for heating
How to choose a pump?
Since this device is so important for the heating system, you need to seriously consider its choice. In order to determine what equipment is suitable, you should first examine your needs. It is necessary to answer some questions.- What should be the temperature in the room?
- How many common areas do I need to heat?
- What kind of fuel will be used?
- What are the characteristics of the boiler?
What are the most important indicators of a pump when buying?
- Pump head. What should be the figure depends on the length of the heating main, the number of radiators and pipe bends. Therefore, the more these nuances, the higher the indicator should be. Since the formula for calculation is very complicated, it is better to consult a specialist, providing him with the necessary data on the system.
- Pump capacity. There is a formula for the calculation: G = Q / (1.16 x DT). Here Q is the need for a house in thermal energy, converted into watts. For this, the area of the room can be multiplied by 100. 1.16 is the specific heat of water. DT is the heat that is needed in the house. Most often 20 ° C.
How do I install the pump?
In order to properly install this equipment, you need to have tools. More often than not enough conventional locksmith devices. Also you will need to buy additional instruments for the pump. These include:- bypasses,
- "American" - threaded connections,
- filter,
- check valve.
- The device is installed near the boiler, on the return pipe.
- It is good to install a filter near the pump. Do not save on this device, as it will not allow the pump to quickly fail.
- Cutting fittings are also very important. If it is not installed, then to remove the pump for repair, you have to disconnect all the heating.
Expansion tank
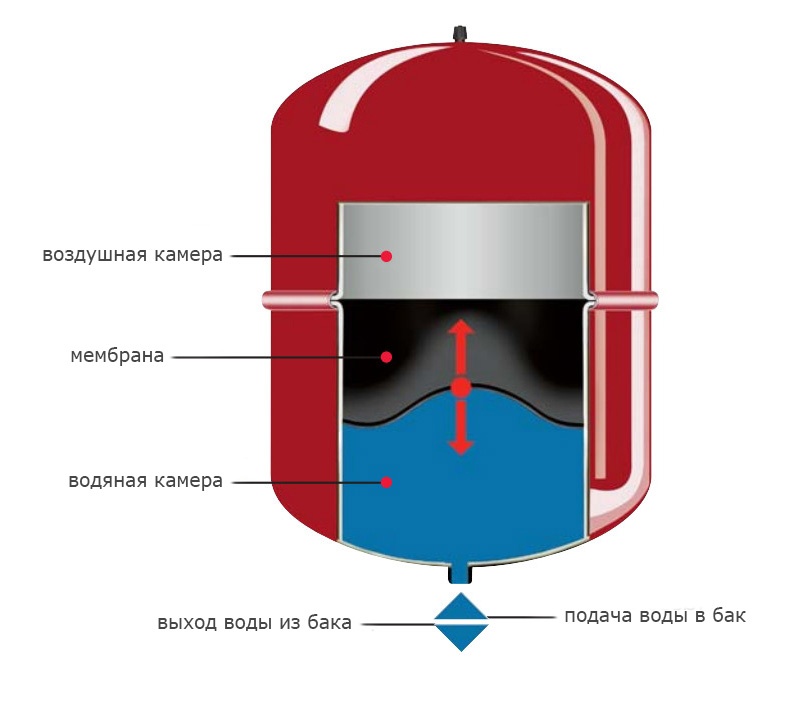
It is impossible to overestimate the importance of this device in the heating system. Water has the property of increasing in volume when heated, and cooling to decrease. Therefore, on the one hand, having heated up, it can create pressure on all nodes of the highway. Because of this load, the entire heating system will not last long. And if the water is simply drained, then when it cools down and the volume decreases, air bubbles form. For this, an expansion tank is needed. When heated, excess fluid enters it, and when the temperature becomes lower, the coolant returns to the pipes. expansion tank
expansion tank
How to choose an expansion tank?
Incorrect selection of this equipment can also lead to problems in the operation of the heating system.Immediately it is worth noting that there are 2 types of tank.
- Open tank. This is a metal open tank. This option is used less and less, as the liquid gradually evaporates from the tank, and it is necessary to add it regularly. If this is not done on time, then air bubbles are formed.
- Closed or diaphragm tank. It is popular because it does not require care. Its device allows you to take the coolant out of the system and return it without interfering with air and avoiding evaporation.
- Deciding which option to choose, you need to determine the volume. This, perhaps, is the most important parameter, which will not forgive mistakes. If you buy a tank with insufficient capacity, then there will be pressure on all nodes of the highway, which will lead to breakdowns. How to calculate the volume correctly? In general, it is advisable to buy a container with a liquid capacity of 10-12% of the volume of the heat carrier of the entire heating system. Here you should take into account not only the water in the pipes, but also do not forget about the radiators, the boiler and so on.
- At last it remains only to determine the manufacturer and the price of the unit.
Installing the expansion tank
If we talk about the installation open tank, it is important to install it at the highest point of the heating main. It is mounted in the outflow pipe of the system.Tank installation closed type more difficult. Here it is necessary to adhere to some basic principles. Here is the step-by-step instruction:
- choose a place, always free to access,
- mount on the wall of the unit should be very reliable, given that its weight will vary,
- deploy it with such a side that all the regulatory mechanisms are easily accessible,
- connects measuring counter, then a pressure reducer, then a safety valve,
- at a temperature below zero, the tank should not be installed.
Security group
This is another useful component of heating with forced circulation. As the name implies, their task is to ensure the safety of the heating system. This equipment consists of three devices. security group
security group
- Safety valve. This is an important device that is tuned to a certain level of pressure in the system. When this value is exceeded, the valve is triggered, saving all parts of the main line from overload and breakage.
- Air vent. Here the name speaks for itself. This device reacts instantly to excessive air release in the system, which leads to an overload of the entire trunk and the failure of its parts.
- The manometer. Its task is to measure the pressure. This is a very important function, because visually the user can not control the system load level. You can focus on the indicator of the maximum pressure indicated for the boiler.
Mounting Features
Proper installation must be carried out to ensure correct operation of the equipment. There are some good tips.- Composite devices of the safety group can be installed both separately and in a joint housing.
- Mount it should be on the pipe that comes out of the boiler.
- The boiler must be below the safety valve.
- A pressure gauge is placed from the boiler, then a safety valve, and then an air vent.



