Marking of flexible cables and wires. Marking of electrical wires and cables - what you need to know for choosing
Generally accepted letter types of marking of wires and cables, characterize the products according to the type of destination, regardless of their manufacturer. Marking letters and numbers indicate different properties of wires and cables: conductor and insulation material, cross-section and number of cores, heat resistance, wear resistance, flexibility, etc.
Electrical wires are made of copper (Cu) and aluminum (Al), they can include one or more wires. Copper wires are most commonly used, which withstand high loads and have greater flexibility. Aluminum, more fragile and with less conductivity, but because of a lower price, they are common during electrical work. For better insulation protection of electric wires, plastic (PVC) and rubber are used. Also, the wires can be bare, i.e. not insulated. For outdoor works and laying of power supply leads, power wires are required in the houses, and for copper wiring and radioelements connecting the copper installation wire. Uninsulated wires are most often used for the installation of air wiring, as well as uninsulated copper wires are used for the manufacture of certain types of antennas and for installation works in closed electrical installations. Still, the wires are specialized, only for specific narrow areas, for example: fire alarm, telephone, usb, antenna, compensation and welding wires and others.
Correct reading of the markings.
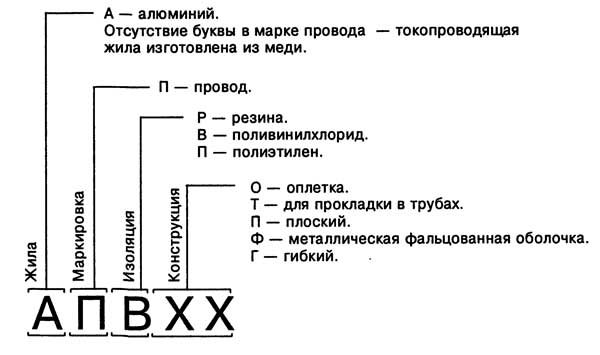
The marking of the wires consists of several groups.
Conditionally denote this: АПВХХ
- The first group of letters - the material of veins - "A" is aluminum. For copper wires this designation is absent;
- "P" is the wire;
- The next group is the isolation material; "P" is rubber, "B" is polyvinyl chloride (PVC), "P" is polyethylene;
- The next group is the construction. "O" - braid, "T" - for laying in the pipe, "P" - flat, "G" - flexible;
- Next is the number of veins;
- And only then - a section.
For example: APPV 2x4. Aluminum Wire Flat Polyvinyl chloride 2-core 4 mm2.
Or PPV 3x2.5. If there is no letter "A", then the wire is copper. And further: Wire Flat Polyvinylchloride 3-core 2.5 mm2
In some cases, there are also numbers that can indicate the class of flexibility of the wires, such as when marking a wire PV1 and PV3. Here PV3 is a more flexible wire.
Next in the wire ПВ3 10 - "10" - indicates a wire cross-section equal to 10mm2, and accordingly ПВ3 16 - where "16" indicates a cross section of 16 mm2.
Aluminum electric wires and cables.
Let's consider some types aluminum wires and cables.
- APUNP(Al Universal Flat Wire), which has two or three cores laid parallel to, PVC protection. It is intended for electrical installation of low-current devices, up to 250V and frequency of 50 Hz. But, for wiring in homes, it is better not to use such wires.
- APO (Al PVC conductor) - single-core wire, with a circular cross-section of 2.5-120mm². APPV is a flat multicore wire. The operating voltage is 450-750V. Used in the repair of flexible sections of the electrical circuit, equipment, machines and various mechanisms. The limiting temperature is 70 ° C, the service life is 15 years.
- APR (Al Wire with Rubber Protection) has a circular cross-section of 2.5 - 120 mm², ADRM - flat multicore, with a circular cross section of 2.5 - 6 mm². It is used for laying in pipes and wooden premises.
- APRN (Al Cable with Rubber Insulation in Non-Flammable Sheath) - solid conductor, cross section from 2.5 - 120 mm². It is used when laying in dry rooms and on outdoor open areas.
- ABBG (Al power cable in a PVC sheath) - stranded wire with a circular cross-section of 2.5 to 50 mm², a temperature limit of 80 ° C, a service life of 30 years. It is intended for dry and damp rooms, open spaces, on the routes of various types, in fire-hazardous and explosive areas.
- AVRG (Al cable Flexible in PVC sheath with Rubber insulation) - can have up to 4 cores, cross section from 4 - 300 mm². Rated voltage 0,66 kW, constant 1,0 kW, frequency 50 Hz, temperature t 200 ° C, service life 30 years. Used in areas where there are increased requirements for resistance against short circuits, dry and damp areas, on bridges, canals, mines, overpasses.
Copper wires and cables.
- Characteristics of the brand wires PV1, PV2, PV3, PV4 (Cu Wire in PVC insulation) the figure denotes, the class of flexibility. Cross-section from 0,5 to 120mm², voltage for networks from 450 - 750V, frequency 400Hz. They can be single-wire and multiwire, they have many modifications and a huge range of applications: plants, machines, houses, trays, plastic pipes etc.
- PPV (Cu Flat Wire with PVC insulation) - two and three core, has a separating base with a cross-section of 0.75 - 4 mm², temperature up to t 70 ° C, voltage for networks from 450 - 750V, frequency 400Hz. It is used for installation of power lighting networks on walls, as well as for laying in channels, pipes.
- PVA (Cu Wire with Stranded veins in PVC braid) with cross-section from 0,5 to 2,5mm², PRS - cross section from 0,5 to 4 mm² - flexible wires with copper cores (2-3). Used mainly for household appliances, extension cords, vacuum cleaners, etc.
- PPP, BSPP (Cu Wire with PVC insulation) - two or three core copper wire with cross-section up to 4 mm². Widely used in low current devices.
- MGSH (copper electrical Flexible Wire Mounting with Silk insulation) with a cross section of 0.5 - 0.12 mm². MGSVV a single-core flexible cable with a cross-section of 0.12-1.5 mm². It is used in electronic devices and interconnections.
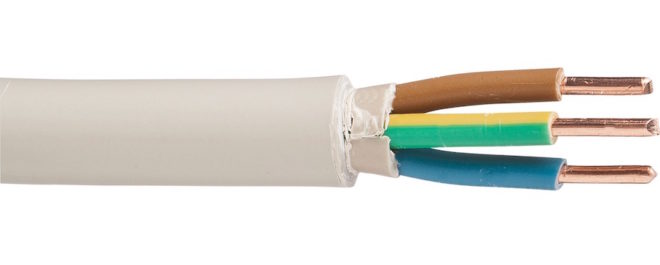
- VVG (Cu power cable in a PVC sheath and with PVC insulation), which can have from one to four cores, a cross section of 1.5 to 502 mm². It is used to lay networks on the street in shadow areas. Double cable insulation allows you to mount wiring in ceilings and partitions of rooms without a cable channel, make wiring.
- VRG (Cu Flexible cable with Rubber insulation in PVC sheath) - cross section 1-240 mm², can have 1-4 cores. Used for air laying, in various types of rooms, bridges and electric racks.
- NWG (Cu Flexible power cable with Rubber insulated protection in Rubber Non-flammable braid) has a circular cross-section 1-240mm², frequency 50Hz, rated voltage 0.66kW, constant 1.0kW, service life 30 years. It is used in mines and canals, in premises with a high probability of flooding.
For conducting wiring in the house it is better to use copper wires. They are more flexible, less breakable during installation, less oxidized, soldered in the usual way, have better electrical conductivity.
The purpose of the winding wire.
Winding wires are used for making windings of electric machines and devices, as well as in the production of radio engineering products, TV elements, etc. Such wires are made of copper of high purity with good conductivity.
Here are some of their brands:
- PETV - (Winding wire enamel heat-resistant with enamel insulation), is a copper wire-wire, diameter 0.063 - 2.500 mm2. Enameled wires are highly resistant to heat (up to 120 ° C) and do not need to clean the insulation.
- The wire PETV2 where "2" is the number of layers of lacquer on the wire. The diameter of PETV2 is from 0.08 to 5 mm2. Used for winding power motors, engines for home appliances and tools, transformers, measuring instruments, coils and relays.
Cables and wires of narrow specialization.
- TRP (Cu Telephone Ratification in PVC insulation) - two-core with a separation base, section 0.4 - 0.5 mm². For laying telephone network. The so-called telephone noodles.
- CPSN (A) - FRLS, KPSG (A) - FRHF, KSSng (A) - FRLSLTx - these are special low-current cables for mounting fire alarm and fire protection system. Explanation: ng - non-burning, (A) - category, LS - low smoke formation, HF - low oxidative activity, LTx-with low toxicity, KPS-fire alarm cable. In accordance with regulatory documents GOST 31565-2012 (GOST R 53315-2009), only such cables can be used in the fire protection system. The wire for signaling must be particularly tenacious, otherwise the security system will not respond in time. These wires are manufactured using the latest technology in the field of cable production for fire protection and alarm systems.
Before the entry into force, in 2009 the Federal Law No. 123 "Technical Regulations on Fire Safety" successfully used fire cables KPSVV and KPSVEV, in braided red. Now they can only be used for burglar alarm systems. - USB cable. All multimedia devices and gadgets are equipped with a USB connector. USB 2.0 is high-speed and consists of a single twisted pair of 28 AWG for data transfer and two power conductors from 20 AWG to 28AWG. All usb cables are filmed, and have a ferrite ring, which serves as a filter. The length, maybe up to five meters.
- Antenna coaxial cable for the TV. It has an electrically conductive braid (shield) and insulation of a certain thickness. That's why it turns out to be thick (about 6 mm²). The braid protects it from electromagnetic and electrostatic interference, reducing losses to a minimum. Has a wave impedance of 75 ohms. For better reception, the central core of the television antenna cable is made of copper, and the screen can be made of both copper braid and aluminum foil. Main types of brands RK 75, RG 6, RG 59, SAT 50, SAT 703, DG 113 are used, both for analogue, and for cable TV and satellite antennas. To connect to the TV, use the F-plug.
Wire for welding machine.
COP - the marking stands for simply - the welding cable. The letter "P" indicates that the wire has polymer protection, a combination of the letters "HF" (high frequency) "PP" (alternating and direct current). The cable for the welding machine is copper and is resistant to t ° 50C. , and has a special. insulation from hose rubber for protection against short circuit, not combustible. Section 10-70 mm², working voltage 600V, frequency 400Hz.
Types of marking cables for connecting the welding machine:
- KG-T, is used to work at elevated temperature. t up to 85 ° C.
- KG-HL, contains a special cold resistant rubber (t to -60 ° C).
- COG1 has increased flexibility.
Electric wires are decorative.
the wire - different kinds of wires used, both in houses for wiring and on the street, executed in original form. Cross-section from 0,5 to 2,5 мм², the shell, more often, silk. Externally the decorative retro electric wire looks in the spirit of the old time and consists of two twisted wires. The retro wire is used by designers in houses from a wooden beam and looks pompously and majestically.
Decorative wires are widely used, and have a variety of modifications. In the interiors of clubs and entertainment, you can meet glowing neon, multi-colored wires. Decorative braids allow performing work of any complexity not only qualitatively, but also beautifully.
The whole modern world is enveloped in wires. In houses, on walls, on roofs, on street lamps, under the ground are laid lighting, high-voltage wires. The cord of the iron, vacuum cleaner, coffee machine, washing machine, computer, TV, refrigerator is pulled to the outlet to connect the power. The high-voltage line, through the deserted taiga, carries electricity to cities from hydroelectric power stations from Siberian rivers.
The marking of cables and wires of an inexperienced buyer can lead to a difficult situation. The brands of cables and wires indicate a certain way so that you can easily choose among different types of products. The letters indicate: what is needed for the wire, where it will lie, from which metal the central core is made, from which the insulation, to what capacity is calculated. In order to avoid fires, electric wire or the cable must be selected correctly. On how to read the brand of wires, we will tell in this article.
What are the wires

By wire today, telephone calls, all kinds of information, electric power of industrial sizes and households are transmitted. Depending on what kind of work the wire does, it differs by different metal and core diameter, number of cores, insulation, special qualities. In places of increased fire danger, for example, lay cables or cords with insulation that burns badly. All these nuances have a certain designation in the form of letters and numbers indicated on the insulation electrical wires.
Explanation of the marking of wires is a short enumeration technical specifications products. Each letter of the marking indicates:
- metal, from which the central veins are made, directly passing an electric current;
- place of application of this product;
- insulation material and common shells, additional protection;
- degree of flexibility, resistance to fire, self-fading ability, low smoke emission, non-maintenance of combustion;
- type of construction, number of cores;
- the total cross-section area of wires, veins;
- the optimum voltage that the product can withstand in the operating mode.
Product groups
Today, cables are used for electrical wiring, conventional wires and household cords. These are the three main groups on which the electrical products can be divided conditionally. Depending on the purpose, they are made with different number of cores and cross-section of the electrically conducting core, they are differently insulated. For example, if you decide to install a fountain in a summer pond, the cable laid under the water should be insulated in a special way.
The wire

One or few wires without insulation, or with a thin insulating film, are called a wire. Some experts simply call them residential. Wire insulation is usually light, not metallic. This is varnish, polyvinylchloride. Isolated with varnish the vein is used for the winding of transformers, motors.
Two-wire wire with PVC insulation is laid when installing domestic electrical wiring in multi-apartment buildings, in the country, in wooden buildings, country cottages.

The wires are produced mainly with a copper and aluminum core. Although there are veins of steel and other expensive alloys. The wire with copper cores is more expensive than aluminum, but it is capable of passing a current of higher values. This provides better fire safety because the wire does not heat up. What should be taken into account when doing electricity wiring in a wooden structure. Copper cores are capable of experiencing more bends without breaking than aluminum ones.

Although aluminum wires cheaper, but they are more fragile, so they are sold and used less and less. Copper and aluminum are oxidized in the open air. Therefore, the connections should be carried out through the terminals or well insulated, tinned, varnished.
Contacts can be insulated and bare. The open view is used on trolleybus wires. The insulated wire is made protected and without additional protection, it is a layer of plastic, rubber, for example, for laying in a damp room, such as a bath.
Also, the wires are divided into power, installation, installation. Mounting - copper, lay in electric boards. Mounting wires connect parts in different devices. Power and installation are used outdoors and inside the dwelling. Products that are under voltage of 220 volts are called power wires, they are laid in any house from outlets to light bulbs and household appliances.
Cable

This product is made of solid or stranded insulated wires, covered with a common sheath of plastic, rubber, vinyl. The cable can be closed by armor, for protection against vandals, this is indicated in the cipher printed on the insulation.
Cable, in turn, happens:
- control;
- power;
- analog;
- telephone;
- radio.
Power cable transmits electricity to distribution boards and lighting devices, water supply pumps. It is laid on the street, through the air and underground, as well as inside private and industrial buildings. Such an article happens with an aluminum core and a copper one. Today more often use a copper variant. The insulating layer is made of rubber, vinyl, different polyethylene.
The control cable is capable of transmitting an information signal to control different devices. This cable can also be copper or aluminum.
An analog cable is used in various automation networks, usually a copper wire with a protective braid. The shield from the braid protects the information signal from various interference.
Cords

Cords in everyday life are called two-wire and stranded wires, which connect electrical appliances, lighting lamps to the power network in 220 V, frequency of 50 Hz. A two-wire wire is used where there is no need to mount a special earthing. Today, cords with euro-plugs include refrigerators, irons, hairdryers, microwave ovens, washing machines, electric kettles, coffee machines. Various extension cords are also constructed from cords capable of withstanding a large load from several household appliances. They are best made of three copper strands, flexible and capable of carrying a high current.
How to decipher the marking of domestic producers
Every person, intending to purchase wires, cables, faces a difficult task of choice. This is because the labeling of wires indicated on the insulation looks like a cipher. Knowing what those letters and numbers indicate on the insulation of electrical products, you can easily go to the store and buy the product you need.

Consider examples of marking, with decoding, so you can buy products for electrical wiring that meet the specifications. The old wiring today does not cope with the connection of new household equipment.
Power cables are marked as follows:
- A - this letter tells about what metal is made of conductive core. If you see the letter A in the first place of the cipher of the marking, then the current carrying wire is made of aluminum. When lived from electrotechnical copper - in the first place there will be no letter;
- AA - on the first two positions informs the buyer - aluminum core in an aluminum shell;
- B - informs about the presence of armor from 2 steel plates with anti-corrosion protection;
- Bing - armored, not lit;
- B - the symbol can be indicated in the first position, it claims to be insulated with polyvinyl chloride;
- B - the symbol can appear in the second position, it informs in this case about the presence in the cable of the second layer of PVC;
- The D - symbol can be indicated at the end of the letter part of the cipher, it reports that the wire is bare, without additional protection;
- K - the letter informs that the armor of the cable is made of round steel wire. On suburban area Wiring can bite rabbits, other wild animals, for this, there are cables covered with armor;
- Шв - availability of the pressed PVC hose on the armor;
- Шп - a layer from the pressed hose on an armor, from polyethylene;
- P is the rubber layer;
- HP - rubber, does not burn;
- PS - self-extinguishing polyethylene, which is important in hazardous areas for ignition;
- Pv - the polyethylene is vulcanized;
- ng - symbols indicating that the cable does not burn itself and does not support combustion in the group;
- LS - Low Smoke - produces little smoke;
- ng - LS - does not burn, does not emit smoke;
- FR - increased resistance to fire, the presence of a mica-containing plate;
- FRLS - little smoke, resistant to fire;
- Ш - sometimes there is such a marking, meaning a cord.
It should be noted that only the first letter A indicates the metal of the vein. If it is not in the marking, then the vein is made of copper. All other letters denote insulation material, protective shells and their properties, such as resistance to fire, the ability to self-damp, do not emit a large volume of toxic smoke. If such a cable is laid in a group of others, it does not support combustion. In the cipher of the marking this is marked with small letters ng.

On the control cable marking is applied as follows:
- A - the symbol placed on the first position, asserts that the vein is aluminum, when A is missed, copper wire;
- B - on the second position, without A - on the first, indicates that PVC insulation;
- B - in the third position, when there is no A - on the second, speaks of an additional layer of PVC;
- P is polyethylene;
- PS - polyethylene self-damped;
- D - no additional protection;
- P is rubber.
All symbols except A report layers of protection. Where high dampness and temperature, for example, in a bath, protection is needed from rubber, self-damp polyethylene.

Marking typical for installation:
- M - at the first position, designates the mounting wire;
- D - many wires, if there is no symbol, one wire;
- B - PVC;
- PV-1, PV-3 - PVC layer, figures 1 and 3 indicate the degree of flexibility;
- PVS - PVC, wire for connection;
- ШВВП - flat cord, two layers of vinyl;
- PPPP - wire universal wagon;
- PUGNP - universal wiring wires, high flexibility. Pave inside the premises, for household equipment and street lamps.
Popular markings
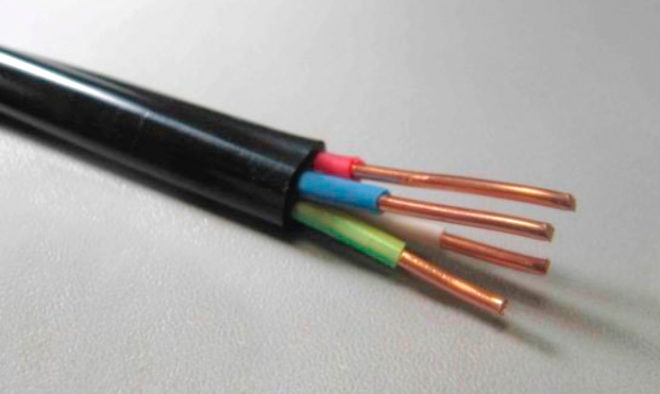
A popular type of cable - VVG - is read: Vinyl, Vinyl, Naked. If you look at all the letters in more detail, you get:
The first symbol is missing, hence the core is made of electrical copper.
B - insulation of each core is made of PVC.
B - all veins are surrounded by a common polyvinylchloride dense layer.
D is bare, that is, there is no armor over the common shell - an anti-vandal rigid structure.
The VVG cable has one to five current-carrying parts. He can have zero vein or be absent.
If the cable is marked VVGng, this means that this subset of the product does not support the spread of fire. This quality is important for places with an increased risk of fire.
More complete marking: VVGng cable - 0,66 kV 3 * 1,5. The product is copper, made of three cores, each has a cross section of 1.5 mm2. Everyone in PVC insulation (the first symbol B), the general shell is also vinyl (the second symbol B), armor is not (the letter D), does not support burning, being in the group (ng letters).
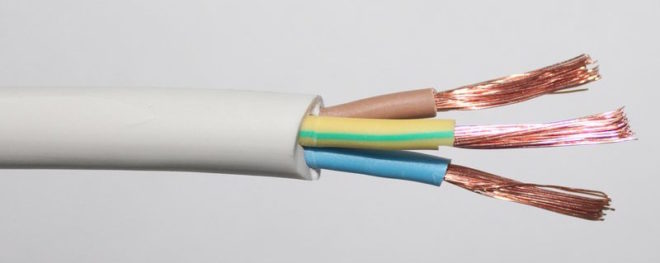
Copper cable PVS is often bought for wiring in private homes, for various equipment in the country, connecting to the network of any kitchen appliances and machines.
The marking of PVS stands for copper wire, connecting wire, with PVC insulation. Such a wire is made of 2-5 copper, twisted, separately coated PVC, veins, with different sections (0.5-22 mm2).

Wires on poles are designated as follows:
- SIP-1 - self-supporting insulated with cross-linked polyethylene wire with uninsulated zero;
- SIP-2 - zero core is isolated;
- SIP-4 - insulated conductors with the same cross section.
NYM wires are manufactured according to the German Normenleitung cable standards, in PVC (Y), it is used in various mounting applications. The VDE symbols guarantee the uninterrupted operation in rooms with high temperatures, fire hazardous locations.
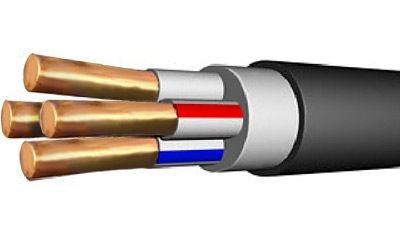
KG - flexible cable is produced with copper round veins, from one to five, with a wide spread of cross-section: from 1 to 185 mm2. The insulation of the veins consists of rubber based on natural rubber (RTI-1). The common shell - hose rubber РШТ-2 or РШТМ-2 from synthetic rubber (isoprene, butadiene).
Foreign producers
If the cipher on the insulation you see Latin letters, then the product of a foreign company.
Power cables for them are designated as follows:
- N - manufactured according to the regulations of the German electrical union VDE;
- Y - in our - vinyl;
- H - no dangerous inclusions, such as halogens;
- M - conductor for installation.
For control:
- Y is isolated using vinyl;
- SL - for control;
- Li - many veins made by VDE.
For installation:
- H - HAR approved;
- N - meets the standards of the country of manufacture;
- 05 - maximum permissible U = 500 V;
- 07 - the maximum permissible U = 750 V;
- V - is insulated with vinyl;
- K - the core is well bent, recommended for installation work.
Foreign marking differs little from the domestic marking, but symbols can be placed in it differently, be careful, consult with experts.
conclusions
If you decide to mount the wiring in your house on your own, make the correct calculation so that the load does not exceed the allowable one. Consider that in the future you can buy a new refrigerator, washing machine, dishwasher, toaster, steamer, multivark, electric oven and other household helpers, with a powerful electricity consumption. Wiring for lighting lamps can be made from simple two-wire wires. Washing machine the machine must be connected directly from the switchboard, with a separate cable designed for high current, through the emergency shutdown device, with mandatory earthing.
Then determine the place of installation, mark the way of passage, measuring the total length. Cable only buy from certified sellers, considering the number of phases, the calculated cross-section, the way of laying. Go to the store with a caliper to clarify the thickness of cores and protective shells. Foreign manufacturers often produce veins with a low cross section.
To facilitate the assimilation of information it is desirable to know the following concepts:
- A vein - a part of a wire or a cable conducting an electric current;
- Insulation is the dielectric protective surface of the cable;
- Monolithic vein - a vein consisting of a single wire;
- Composite core - consists of several wires twisted into a beam (more flexible than a monolithic wire);
- Terminal - clamp intended for.
Materials from which the cable consists, their combinations.
As a conductor, as a rule, either copper or aluminum is used. Each guide has its own advantages and disadvantages. Aluminum is much lighter than copper, however it is a more active chemical substance, and if aluminum wires are connected to copper, then the connection site will quickly break down, so it is necessary to use terminals.
Also, when connecting two aluminum wires, nuts and bolts are usually used. Copper wires is heavier and more expensive, however, copper is more stable, its conductivity is higher, it lasts longer alternating loads and therefore copper wires are most often used for laying cables in houses and apartments.
Types of copper wires
There are different brands of cable. Two, three, and stranded wires with several layers of insulation are usually used. Copper wires, which are used for the installation of internal electrical wiring, are divided into the following types:
- Flat form, two or three veins, a monolithic vein, double insulation. Are laid under plaster;
- Round, three-core, triple-insulation, monolithic vein. It is laid in screed and in pipes on the surface and under the ground;
- Round, five-core, triple-insulation, monolithic vein;
- Round, three and five-core, double insulation, lived a composite. They have good flexibility and are used in the installation of gypsum board, however, there is a possibility of damage to the wire by the fasteners.

Types of cables and wires
Protection
In some wires, in addition to the insulation layer, there is also protection against physical interference, such wires are called protected. Accordingly, unprotected wires are called without such protection (for example, VVGng). Also there are armored, temperature-resistant, waterproof, protected from external pressure, and many other types of wires and their insulations for different purposes.
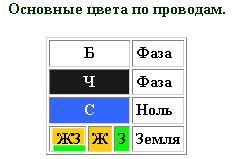
Classification by color
There are colored and one-color veins. The color system was introduced for relief. The color depends on the role played by the veins (phase, neutral, grounding). If a red wire fits the switchboard or the generator, then it acts as a phase, if it's blue or neutral, and if it's green-yellow, then ground.
In the case of single-colored cores, the role of grounding is played by the average.
Types according to the purposes of operation
Mounting wires are used in various electrical engineering, shields, etc. Power and installation are designed for laying electrical wiring.
The difference in the size of the cross-section of the veins (in square millimeters) is from 0.35 to 70 and more.
In ordinary residential buildings, the outlet networks are usually made with wires with a cross-section of 2.5 square millimeters, lighting networks - 1.5 mm2, and for connection of powerful modern electrical appliances it may be required and 6 mm2.
This is due to the fact that the maximum possible amount of electric current depends on the size of the cross-sectional area. The larger it is, the greater the current passes, while not heating the wires to dangerous temperatures.
The most common cause of fires is faulty electrical wiring. In order to choose a wire that will meet the necessary requirements and will not be prohibitively expensive, you need to know what is. All characteristics of the wire are encrypted in a special code consisting of letters and numbers. The decoding of this code is very simple.
Decoding of the marking
With the help of letters, the material from which the insulation and core is made, the purpose of cable operation, the design features are encrypted. All of them go in a certain order, each has its own meaning.
And with the help of numbers you can find out the number of cores, if the cable is stranded, and their cross-section.
For standard, non-specific for some areas, the letters of code consist of four specifiers.
The first letter shows what material the veins are made of. If the letter A, they are made of aluminum, and if made of copper, then the letter is not put (for example: ABBG - aluminum core, BBG-copper).
The second letter deciphers the purpose of the cable. "K" - control, "M" - mounting, "P (U)" or "W" - installation, "MG" - flexible mounting, if there is no letter, this is the power cable.
The third letter shows what type of insulation is used. "B" - polyvinylchoride, "D" - double winding, "K" - kapron, "P" - polyethylene, "P" - rubber, "HP" or "H" - non-flammable rubber, "C" - glass fiber, "Sh "- polyamide silk," E "- screened material.
Finally, the fourth letter shows design features cable. "B" - armored with ribbons, "G" - flexible, "T" - laid in pipes, "K" - armored with a round wire, "O" - in braid. There may be additional designations that are written in small letters (for example, VVGGG means that it is a non-combustible VVG). 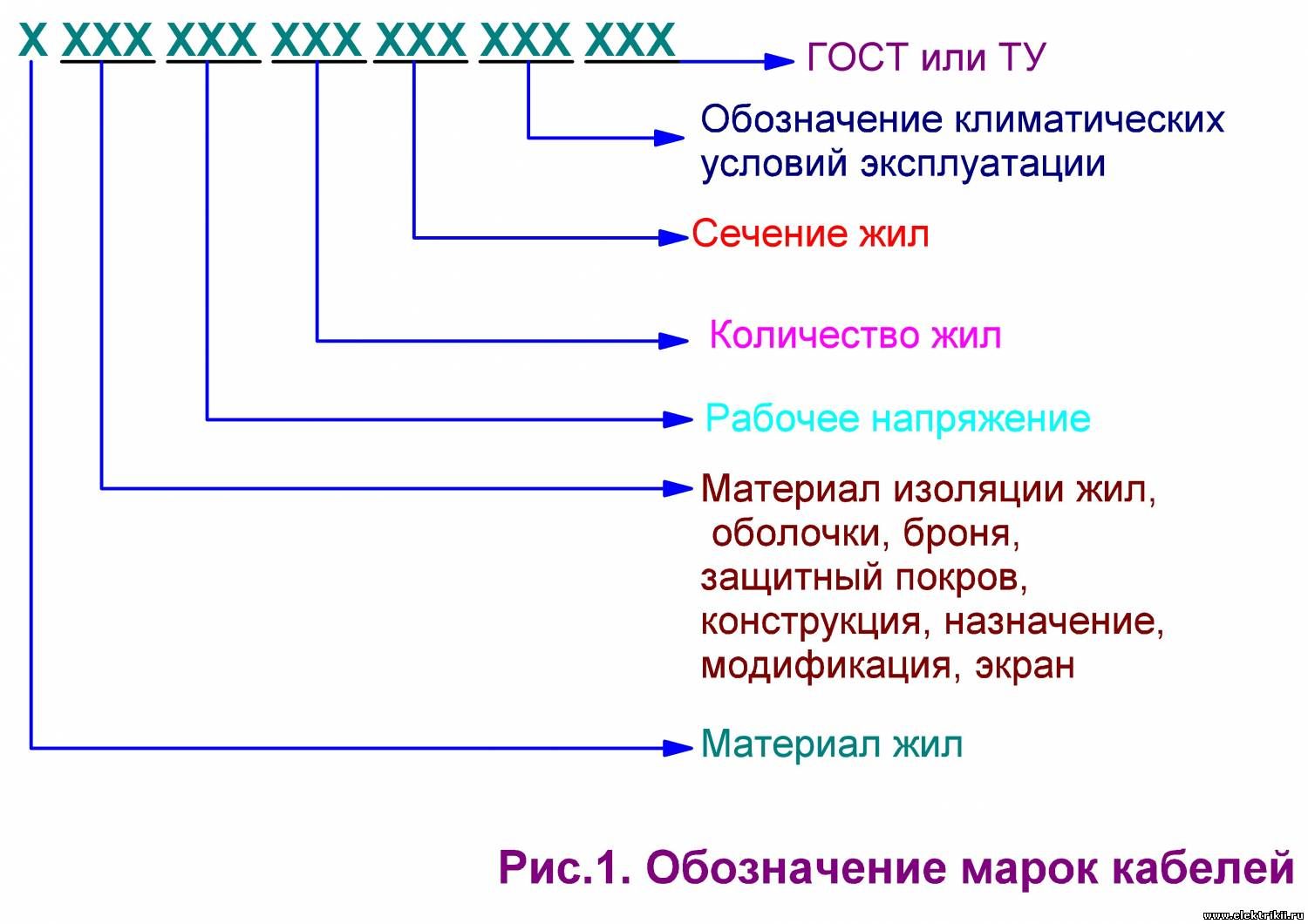

But with the numbers everything is much easier. The first figure shows the number of cores of which the cable consists, and the second dimension of the cross-sectional area (for example, PVA 3x3 means that it is a three-core cable, with a cross-sectional area of each individual core of 3 square millimeters).
The cable marking may contain additional alphabetic and numeric designations, especially in the last decade, when the range of this product has increased significantly.
Decoding code on the example VVGng:
- Letters A, no, then the vein is made of copper;
- There is no letter combination from the second point, which means that there is no second letter, and that in turn means that VVGGG is the power cable;
- Sheath and insulation made of polyvinyl chloride (BB);
- the modification of ng, as already mentioned, means that the material is fireproof.
It is worth noting that this marking of wires is used in Russia and other CIS countries, it differs from imported products.
What is a power cable (SK) and the most common types of SC
Power cables are used for laying electrical wiring outside and inside the premises.
The structure of the power cables consists at least of a conductive core (TPG), the insulation of the conductor and the sheath. Also, there may be all kinds of additional security elements, etc.
One of the most common cables in the last decade has been VVG and its various modifications. VVG consists of a conductive copper core, with a sheath and insulation made of polyvinyl chloride. It is used to distribute an electric current with a voltage of 660-1000 volts and a frequency of 50 hertz. The number of cores can be different, from one to five and a different section from 1.5 to 240 square millimeters. But, of course, in the household conditions a much smaller range is applied (from 1.5 to 6 mm2 in apartments and up to 16 mm2 in private houses). In VVG, the wires can be monolithic and multiwire.

This cable is widely used due to its universal properties. VVG is cold-resistant and can be used in various environmental conditions, outdoors (but not on the ground), at high altitudes and under water. Modification VVGng is used in fire hazardous areas, these cables can be laid in bundles, they still will not burn.
Unlike VVG, the modification of VBGG has in addition to polyvinylchloride insulation also halogen substances, because of which the combustion process is impossible. As well as ignition of the envelope of WWGng veins, gas and smoke are not released.
It is VVG, VVGng and NYM that are most often used for the electrification of a private house or apartment. NYM is a foreign analogue of VVGNG, which has additional protection for bends. These cables can be used for open wiring and for hidden. Can be hidden in plaster. However, NYM (like VVG) is afraid of direct sunlight, so before laying the cable it's worth making sure that they do not threaten it.

Storage of electrical wires
Even the best engineer can not calculate the required length of wires, especially on large objects, so in any case there will be leftovers. Naturally, there is no need to throw them away, with proper storage, VVG cables can remain usable for many years. The remaining cable must be rolled into a ring with a diameter of 30-50 cm and stored at room temperature.