Calculation of the necessary heat for heating. Calculation of the heating system
Of all the currently known options for heating your home, the most common type is individual system water heating. Oil radiators, fireplaces, stoves, fan heaters and infrared heaters are often used as auxiliary devices.
The heating system of a private house consists of heating appliances, a pipeline and shut-off and regulating mechanisms, all of this serves to transport heat from the heat generator to the final points of space heating. It is important to understand that the reliability, durability and efficiency of an individual heating system depends on its correct calculation and installation, as well as on the quality of the materials used in this system and its competent operation.
Calculation of the heating system
Let's consider in detail the simplified version of the calculation of the water heating system, in which we will use standard and public components. The figure shows schematically the individual heating system of a private house on the basis of a single-circuit boiler. First of all, we need to determine its power, as it is the basis of all calculations in the future. We will perform this procedure as described below.
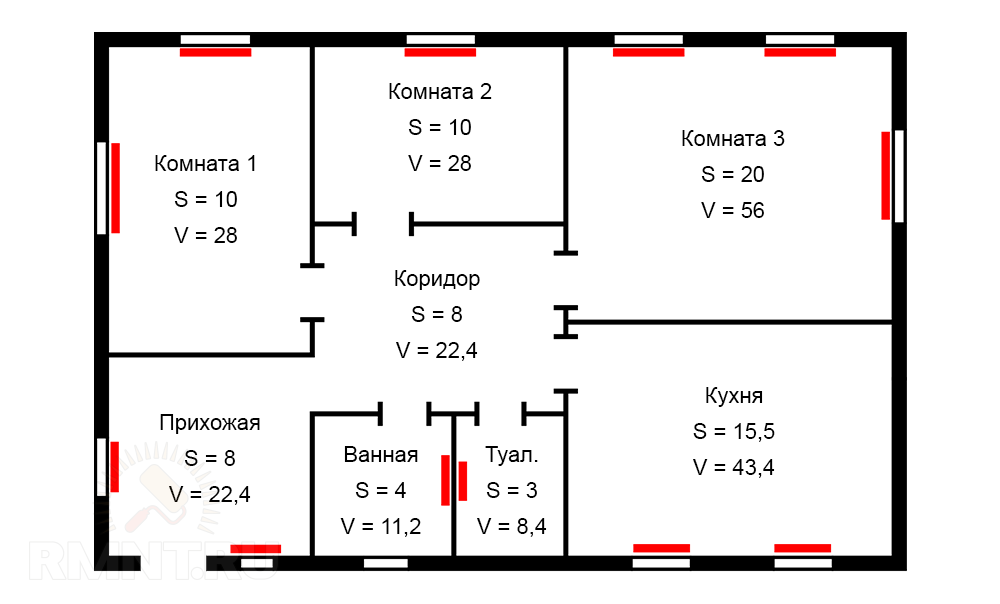 Total area of the room: S = 78.5; total volume: V = 220
Total area of the room: S = 78.5; total volume: V = 220
We have a one-storey house with three rooms, an entrance hall, a corridor, a kitchen, a bathroom and a toilet. Knowing the area of each individual room and the height of the rooms, it is necessary to perform elementary calculations in order to calculate the volume of the whole house:
- room 1: 10 m 2 · 2.8 m = 28 m 3
- room 2: 10 m 2 · 2.8 m = 28 m 3
- room 3: 20 m 2 · 2.8 m = 56 m 3
- entrance hall: 8 m 2 · 2.8 m = 22.4 m 3
- corridor: 8 m 2 · 2.8 m = 22.4 m 3
- kitchen: 15.5 m 2 · 2.8 m = 43.4 m 3
- bathroom: 4 m 2 · 2.8 m = 11.2 m 3
- wC: 3 m 2 · 2.8 m = 8.4 m 3
Thus, we have calculated the volume of all individual rooms, thanks to which we can now calculate the total volume of the house, it is equal to 220 cubic meters. Notice, we also calculated the volume of the corridor, but in fact there is not indicated a single heater, what is it for? The fact is that the corridor will also be heated, but passively, due to the circulation of heat, so we need to make it into the general list of heating, in order for the calculation to be correct and give the desired result.

The next step in calculating the boiler output will be carried out based on the required quantity energy per one cubic meter. For each region there is an indicator - in our calculations we use 40 W per cubic meter, based on recommendations for the regions of the European part of the CIS:
- 40 W · 220 m 3 = 8800 W
The resulting figure needs to be raised to a factor of 1.2, which will give us a 20% power reserve to ensure that the boiler does not constantly work at full capacity. Thus, we understand that we need a boiler that is capable of producing 10.6 kW (standard single-circuit boilers are produced with a capacity of 12-14 kW).
Calculation of radiators
In our case, we will use standard aluminum radiators with a height of 0.6 m. The power of each rib of such a radiator at a temperature of 70 ° C is 150 W. Next, we calculate the power of each radiator and the number of conditional edges:
- room 1: 28 m 3 · 40 W · 1,2 = 1344 W. We round up to 1500 and get 10 conditional edges, but since we have two radiators, both under the windows, we take one with 6 ribs, the second with 4.
- room 2: 28 m 3 · 40 W · 1,2 = 1344 Tues. We round up to 1500 and get one radiator with 10 ribs.
- room 3: 56 m 3 · 40 W · 1,2 = 2688 Tues We round up to 2700 and get three radiators: the 1st and the 2nd on the 5 edges, the 3rd (the side) - the 8 edges.
- hall: 22.4 m 3 · 40 W · 1.2 = 1075.2 W. We round up to 1200 and get two radiators with 4 ribs.
- bathroom: 11,2 m 3 · 45 W · 1,2 = 600 W. Here the temperature should be a little higher, you get 1 radiator with 4 ribs.
- wC: 8.4 m 3 · 40 W · 1.2 = 403.2 W. We round up to 450 and get three edges.
- kitchen: 43.4 m 3 · 40 W · 1.2 = 2083.2 W. We round up to 2100 and get two radiators of 7 edges.

In the end result, we see that we need 12 radiators with a total capacity:
- 900 + 600 + 1500 + 750 + 750 + 1200 + 600 + 600 + 600 + 450 + 1050 + 1050 = 10.05 kW
Based on recent calculations, it is clear that our individual heating system will cope with the load imposed on it without problems.
Pipe Selection
Pipeline for the system individual heating is the environment for transportation of thermal energy (in particular, heated water). In the domestic market, pipes for installation of systems are presented in three main types:
- metal
- copper
- plastic
![]()
Metal pipes have a number of significant disadvantages. In addition, they have a high weight and require special equipment for installation, as well as experience, they are still prone to corrosion and can accumulate static electricity. A good option - copper pipes, they are able to withstand temperatures of up to 200 degrees and pressures of about 200 atmospheres. But copper pipes are different in the installation (requires special equipment, silver solder and extensive experience), in addition, their cost is very high. The most popular option is plastic pipes. And that's why:
- they have an aluminum base, which is covered with plastic on both sides, so that they have great strength;
- they absolutely do not pass oxygen, which allows to reduce the process of corrosion formation on internal walls to zero;
- thanks to the aluminum reinforcement they have a very low coefficient of linear expansion;
- plastic pipes are antistatic;
- have low hydraulic resistance;
- no special skills are required for installation.

Installation of the system
First of all, we need to install sectional radiators. They should be placed strictly under the windows, warm air from the radiator will prevent the penetration of cold air from the window. For the installation of sectional radiators, no special equipment will be required, only a puncher and a building level. It is necessary to strictly adhere to one rule: all radiators in the house must be mounted strictly at one horizontal level, this depends on the general circulation of water in the system. Also observe the vertical position of the fins of the radiator.
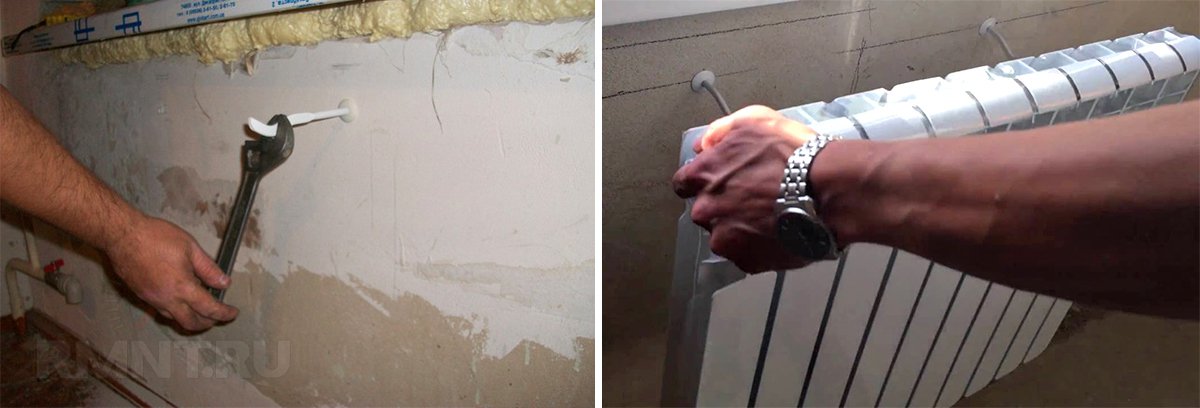

After installing the radiators, you can start laying the pipes. It is necessary to measure in advance the total length of the pipes, and also to calculate the number of all kinds of fittings (elbows, tees, plugs, etc.). For installation of plastic pipes Only three tools are needed - roulette, pipe scissors and a soldering iron. Most of these pipes and fittings have laser perforation in the form of incisions and guide lines, which makes it possible in the place to perform the installation correctly and smoothly. When working with a soldering iron, you should adhere to only one rule - after you have melted and docked the ends of the products, do not scroll them, if at first you can not solder it smoothly, otherwise it is possible to flow in this place. It is better to practice in advance on the pieces that will go to waste.

Additional devices
According to statistics, a system with passive water circulation will function properly if the area of the room does not exceed 100-120 m 2. Otherwise it is necessary to use special pumps. Of course, there are a number of boilers in which pumping systems are already integrated and they themselves ensure the circulation of water through pipes, if you do not have one, you should purchase it separately.
![]()
In the domestic market, their choice is very large, besides they meet all the necessary requirements - they consume little electricity, are quiet and small. Mount circulating pumps on the ends of heating branches. Thus, the pump will last longer, as it will not be exposed to direct hot water.
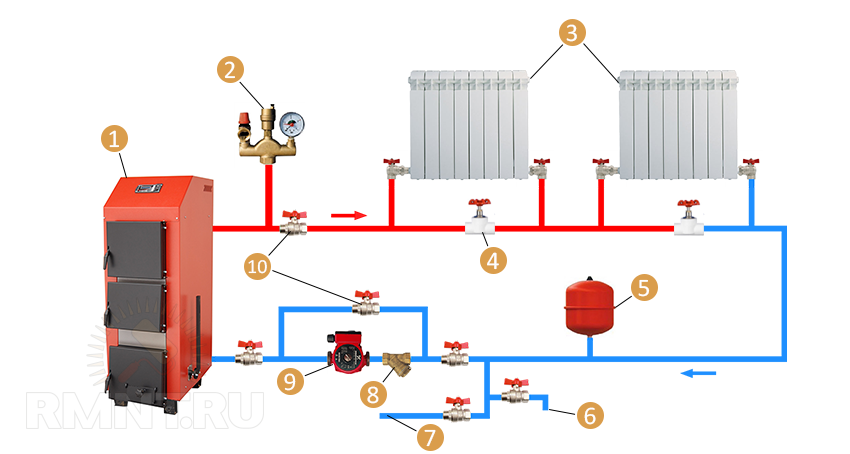 Example of a single-pipe heating system with forced circulation: 1 - the boiler; 2 - security group; 3 - radiators of heating; 4 - needle valve; 5 - expansion tank; 6 - drain; 7 - water supply; 8 - filter coarse cleaning water; 9 - circulating pump; 10 - ball valves
Example of a single-pipe heating system with forced circulation: 1 - the boiler; 2 - security group; 3 - radiators of heating; 4 - needle valve; 5 - expansion tank; 6 - drain; 7 - water supply; 8 - filter coarse cleaning water; 9 - circulating pump; 10 - ball valves
From all of the above, it becomes clear that with the installation of such a system can easily cope with two or three people, it does not need to have special professional skills, most importantly, be able to use basic construction tools. In our article, we examined the system of individual heating, assembled with standard components, their price and accessibility will allow almost everyone at home to mount a similar heating system.
The system of water heating has been increasingly popular recently as the main way for heating a private house. Water heating can be supplemented with devices such as heaters that work on electricity. Some devices and heating systems appeared on the domestic market quite recently, but already managed to gain popularity. These include infrared heaters, oil coolers, a warm floor system and others. To heat a local type, a device such as a fireplace is often used.
However, recently fireplaces perform more decorative function than heating. On how well the design and calculation of private house heating has been carried out, and the water heating system has been installed, its durability and efficiency during operation depend. During the operation of such a heating system, it is necessary to adhere to certain rules so that it works as efficiently and efficiently as possible.
The heating system of a private house is not only components such as a boiler or radiators. A water-type heating system includes such elements as:
- Pumps;
- Means of automation;
- Pipeline;
- Heat carrier;
- Devices for adjustment.
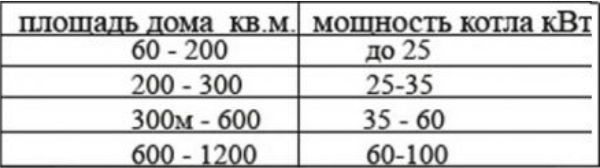
To calculate the heating of a private house, you need to be guided by such parameters as the capacity of the boiler. For each of the rooms in the house, it is also necessary to calculate the power of the radiators.
Boiler selection
The boiler can be of several types:
- A boiler operating on liquid fuel;
- A gas boiler;
- Solid fuel boiler;
- Combined boiler.
The choice of a boiler that will use the heating scheme of a residential house should depend on which type of fuel is the most affordable and inexpensive.
In addition to the cost of fuel, it is required at least once a year to conduct a preventive inspection of the boiler. It is best for these purposes to call a specialist. Also, you need to perform preventive cleaning of filters. The most simple to operate are boilers that operate on gas. They are also quite cheap in maintenance and repair. The gas boiler will only fit in those houses that have access to the gas main.
Gas is a type of fuel that does not require individual transportation or storage space. In addition to this, many gas boilers modern type can boast a fairly high efficiency.
Boilers of this class are distinguished by a high degree of safety. Modern boilers are designed in such a way that they do not need to allocate a special room for the boiler house. Modern boilers are characterized by a beautiful appearance and are able to successfully fit into the interior of any kitchen.

To date, semi-automatic boilers operating on solid fuel are very popular. True, there is one disadvantage of such boilers, which is that once a day you need to load fuel. Many manufacturers produce such boilers that are fully automated. In such boilers solid fuel is loaded in an autonomous mode.
Make a calculation of the heating system of a private house is possible in the case of a boiler operating on electricity.
However, such boilers are a bit more problematic. In addition to the main problem, which is that now electricity is quite expensive, they can still reboot the network. In small settlements, an average of 3 kW per hour is allocated per house, and this is not enough for a boiler, and it should be borne in mind that the network will be loaded not only by the operation of the boiler.

For the organization of the heating system of a private house, it is possible to install a liquid-fuel type boiler. The disadvantage of such boilers is that they can cause criticism in terms of ecology and safety.
Calculation of boiler power
Before calculating the heating in the house, it is necessary to do this with the calculation of the boiler output. The efficiency of the entire heating system will depend on the boiler's capacity, first of all. The main thing in this matter is not to overdo it, since a too powerful boiler will consume more fuel than necessary. And if the boiler is too weak, it will not be possible to heat the house properly, and this will negatively affect the comfort in the house. Therefore, the calculation of the heating system a country house - it is important. To choose a boiler of the necessary capacity it is possible, if in parallel to calculate the specific heat losses of the building for the entire heating period. Calculation of home heating - specific heat loss can be the following method:
q house = Q year / F h
Qgod is the heat energy consumption for the entire heating period;
Fh is the area of the house that is heated;
In order to calculate the heating of a country house - the energy consumption that will leave the heating of a private house, you need to use the following formula and a tool such as a calculator:
Q year = β h *
As it is easy to see, we need an INNER diameter of 20 millimeters, which for polypropylene corresponds to an external diameter of 25 mm.
Conclusion
Some additional information on calculation methods heating systems you will find in the video attached to the article. Warm winters!
A detailed calculation of the heating system of the house with all the features and difficulties is considered, the heating sources that are most often auxiliary are listed, as well as a one-pipe and two-pipe heating system are considered in detail.
Figure 1: One of the home heating systems
Modern sources of house heating
Electric heating devices, which include fan heaters, infrared heaters, oil coolers, heat guns, "warm floors" and others, as well as fireplaces and stoves, are most often used as auxiliary heating sources. A private house with an air heating system - an extreme rarity.It should be noted that there are generally accepted standards for the specific power of the boiler depending on climatic zones:
- W = 1,5 - 2,0 kW - in the Northern regions.
- W = 1,2 - 1,5 kW - in the Central regions;
- W = 0,7 - 0,9 kW - in the Southern regions;
The calculation of the house heating system includes the calculation of the power, during which the following parameters should be taken into account: (See also:)
- S is the total area of the room that is heated;
- W - boiler power (specific) per 10 m 3, which is determined taking into account the climatic features of the region.
1) S = 100 m 2 - the area of the room that is heated;
2) W = 1.2 kW is the specific capacity of the Central Districts.
W cat. = 100 * 1.2 / 10 = 12 kW.

Figure 2: Design of the heating system
Advice! To improve the life of parts, circulating pumps It is necessary to install in a return line, which leads directly to the boiler from the heaters. Thus, it is possible to avoid contact of parts with hot water.

Figure 3: Design of the circulation pump
Requirements for circulation pumps
As the circulation pumps work continuously, there are certain requirements that they must meet:- quiet operation;
- simplicity of operation;
- low energy consumption;
- reliability;
- durability.

Figure 4: Circulation pumps
Features of calculating the heating system
Hydraulic calculation of the heating system is one of the most time-consuming and complex stages in the design of water-type heating systems. Before carrying out the design, it is necessary to perform calculations and graphical works: (See also:)- determine the heat balance of the premises that are heated;
- choose the type of heat exchanger surfaces or heaters, then place them on the plans of the buildings of the room, which is heated;
- make decisions about the configuration and installation of the water heating system: tracing instrument branches and main pipelines, placing the heat source.
- determine the type of pipelines that are used, regulating and shut-off valves (valves, flow, valves, valves and pressure regulators, thermostats); (See also: )
- draw up an axonometric diagram for the given heating system, in which it is necessary to indicate the number, length of the calculated sections and thermal loads;
- determine the main circulation ring, which consists of consecutive sections of pipelines, taking into account the maximum flow of the heat carrier for the two-pipe system (from the source of heat to the most remote heating device) or for a single-pipe system (from the riser back to the source of heat energy).

Figure 5: Hydraulic calculation program
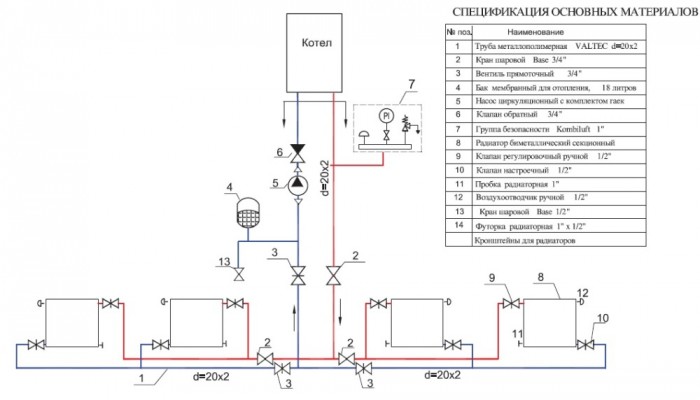
The calculated section of the pipeline is a section of fixed diameter with a stable flow of heat carrier, which is determined by the heat balance of the heated room. The calculation of a two-pipe heating system includes the numbering of the calculation areas, which should start with a heat source (heat generator or ITP). As a rule, the nodal points in the branch lines are allocated in capital letters on the supply line. The corresponding nodes are indicated with a stroke on the collection main pipelines.

Figure 6: Two-pipe heating system
With regard to the nodal points on the risers (in the places where the branch distributing instrument branches branch), they are designated by simple Arabic numerals corresponding to the floor number (for horizontal systems) or they correspond to the number of the riser branch (for vertical systems). These numbers are highlighted in the places where the coolant flows are collected. Each settlement site is numbered by two letters or numbers, which must correspond to the beginning of the section and its end.
Vertical heating system
For vertical heating systems, the numbering of the risers (instrument branches) should be made in Arabic numerals in a clockwise direction, starting from the apartment, which is located on the floor plan in the upper left part along the perimeter of the building. With the help of plans drawn on a scale, the length of pipeline sections is determined with an accuracy of 0.1 m.
Figure 7: Two-pipe vertical heating circuit
Calculation of the heating system of a private house can not do without calculating the heat load of the plot, so it is necessary to determine the heat flow that transfers or has already transferred the coolant to the supply pipes. The heat load of the necessary sections of the pipeline system (distribution and prefabricated) is calculated with rounding up to 10 W, and is determined only after the distribution of the heat load among all appliances and instrument branches that are heated. It is customary to indicate the thermal load of the section - Q i-j (W) above the remote line, and its length - l i-j (m) under the remote line.
The calculation of single-tube systems differs slightly from the calculation of two-pipe systems by a small number of features in determining the necessary surface of heating devices, and also when determining the size and diameter of the closing sections and the leads of these heating devices. The procedure for calculating this heating system coincides with the above example of calculating a two-pipe system.
Calculation of a single-pipe heating system begins with the fact that the diameters of the risers and pipes must be calculated from the pressure. You can also calculate by reverse scheme: Initially find the diameters along the ring of the device, then determine the diameters of the closing sections. With this calculation, the leakage coefficient is determined by the schedule, which is compiled after the results of the conducted studies.

Figure 8: Single-pipe system heating systems
Important! In calculations, it is impossible to use the previously taken amount of water that flows into heating appliances, since this indicator is not fixed and constant, but varies under the influence of various factors.
Use of materials is allowed only if there is an indexed link to the page with the material.



